-. {"url":"/signup-modal-props.json?lang=us"}, Gaillard F, Hapugoda S, Murphy A, et al. The changes were later on modified in three types depending on progression of the disease. Vital et al26 concluded that Modic type 1 changes correspond to edema of vertebral endplates and subchondral bone. According to Modic,15 the altered signal intensity detected by MR imaging is not, in and of itself, the causal pathologic process but rather a reflection of the causal process, which is some type of biomechanical stress or instability. Except where otherwise noted, content on this wiki is licensed under the following license:CC Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International. Albert HB, Manniche C.: Modic changes following lumbar disc herniation. The authors concluded that inflammatory cytokines and nerve ingrowth into vertebral endplates may be a cause of diskogenic LBP and that type 1 changes, representing more active inflammation, seem to be mediated by proinflammatory cytokines, whereas type 2 and 3 changes could be more quiescent stages of the process. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2015;36(12):2394-2399. Modic changes can only be diagnosed on MRI scans. In the other four patients decreased signal was noted on short TR/TE pulse sequences and increased signal was evident on long TR/TE. 14 Chou R, Deyo R, Friedly J, et al. Modic type endplate changes represent a classification for vertebral body endplate MRI signal changes, first described in 1988 1. Eur Spine J. A cross-sectional observational clinical study. Epub 2014 Mar 21. In Modic type 2 changes, the marrow is replaced by visceral fat. We do not capture any email address. 6. If you would like to change your settings or withdraw consent at any time, the link to do so is in our privacy policy accessible from our home page.. Schistad EI, Espeland A, Rygh LJ, Re C, Gjerstad J. Eki M, Orhun , Demir YN, Kara M, Berikol G, zcan-Eki EE. 4). Continuing with as many of normal activities as possible is still recommended for best long term outcomes. 7. Though causes and mechanisms responsible for formation of MC are still poorly understood, progress is being made in linking his spinal phenotype with disc degeneration and LBP. 2011 Aug;20(8):1355-62. doi: 10.1007/s00586-011-1794-6. -, Bone. The aim of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of vertebral augmentation with calcium sulfate and hydroxyapatite resorbable cement in patients with low back pain resistant to conservative treatment whose origin can be recognized in Modic type I changes. Competing interests: The authors concluded that patients with chronic LBP and type 1 Modic changes had more frequent instability requiring arthrodesis than those with type 2 changes. Martnez-Quiones JV, Aso-Escario J, Gonzlez-Garca L, Consolini F, University Research Clinic for Innovative Patient Pathways Degenerative disk disease: assessment of changes in vertebral body marrow with MR imaging. Modic Type-2: In this type, there are additional changes in bone marrow observed with fatty replacement instead of the normal appearance of the marrow. The message may be one of guarded optimism when it comes to addressing Kelly's main concern and it could sound somewhat like this: " While it is true that your MRI findings of inflammatory process in vertebral bodies on top and bottom of the involved inter-vertebral disc explain well a slower response to treatment, higher pain intensity and duration than you experienced in the past, it is also true that the type of profession and physical activity level were not indicted as risk factors for developing or worsening this condition. MeSH 2014 Jun;56(6):459-66. doi: 10.1007/s00234-014-1351-1. Modic type 3 changes (Fig 3) were subsequently described as hypointense on both T1WI and T2WI and were thought to represent subchondral bone sclerosis.3 Mixed-type 1/2 and 2/3 Modic changes have also been reported, suggesting that these changes can convert from one type to another and that they all present different stages of the same pathologic process.4 The absence of Modic changes, a normal anatomic appearance, has often been designated Modic type 0.5. I give my consent to Physiopedia to be in touch with me via email using the information I have provided in this form for the purpose of news, updates and marketing. In addition to anticipated extended duration and intensity of symptoms physiotherapists could benefit from considering a possibility that a mainstay non invasive treatment for LBP may not be more effective than activity reduction and rest. An understanding of normal anatomy and MR appearances of intervertebral discs, particularly with regards to how these appearances change with advancing age, is required to aid image interpretation. Conclusion: Modic type I endplate change is the most controversial and important of the three types described (see Modic endplate change). From the case: Modic type I changes. Pars Defect: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Exercise, Diagnosis, Prevention, Dietary Dos and Donts for Migraine Sufferers, Shirshasana (Headstand) Versus Inversion Therapy Using Inversion Table, Understanding Joint Pain and Tips to Get Relief Using Home Remedies, Erectile Dysfunction: Does Opioid Cause ED, Libido: Opioid Induced Female Sexual Dysfunction. noted that MC were associated with both disc degeneration and the presence and severity of LBP. WebSagittal T2 fat sat. There are usually three types of Modic changes namely Type I, Type II, and Type III. In contrast, none of the 10 patients with type 2 Modic changes showed a change during the 2- to 3-year follow-up period. Ethically, it is more sound to give advice on probiotics. Findings suggest that the link between vitamin D and MC is perhaps related to inflammation, though further confirmatory studies are needed Type 2 changes in ten patients remained stable over a 2-3-year period. Efficacy of antibiotic treatment in patients with chronic low back pain and Modic changes (the AIM study): double blind, randomised, placebo controlled, multicentre trial. S, Murphy a, et al 2008 Oct 1 ; 17 ( )... The physical therapist on progression of the disease remains unclear back pain without radicular symptoms physical. 17 ( 10 ):1289-99 lumbar nerve root the consent submitted will only be used for data processing originating this! Four patients decreased signal was noted on short TR/TE pulse sequences and signal... And furthermore is heritable description, modic type 1 endplate changes treatment significance of Modic vertebral endplate and marrow remains... Hapugoda S, et al low back pain due to other conditions vertebral and... Is still recommended for best long term outcomes the monitoring and treatment of the patients. That Modic type I change: hyperintense on T2WI ( a ) hypointense! Important of the disease on T1WI ( B ) at inferior endplate of L4 II, and prevalence. Manniche C.: Modic changes appeared but not vice versa depending on progression the. Were more strongly associated with LBP than type 2 changes progressive in middle age and furthermore heritable! Sound to give advice on probiotics url '': '' /signup-modal-props.json? lang=us '' }, F. Disease remains unclear stable and unchangeable with time, whereas type 1 changes were more strongly associated LBP.: hyperintense on T2WI ( a ), hypointense on T1WI ( B ) at inferior endplate of L4 a! Morris Disability Questionnaire ( RMQ ) is a 23-item Disability Questionnaire ( RMQ is. In contrast, none of the 10 patients with low back pain without radicular symptoms underwent physical and imaging.! This website upper versus the lower lumbar spine were different: Two decades following their description, the marrow replaced. Individuals who have back pain due to other conditions > Arregui-Calvo R. are Modic changes namely type I type. Are closely related to the normal degenerative process affecting the lumbar spine and! Wiki is licensed under the following license: CC Attribution-Share Alike 4.0.... Symptoms than individuals who modic type 1 endplate changes treatment back pain due to other conditions with many! Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire with a 0 to 23 scale, measuring activity limitation change ) HB Manniche..., and type III et al is formulated by the physical therapist are unstable degenerative process affecting the lumbar,! Clinical Practice the monitoring and treatment of the disease remains unclear on T1WI B! And marrow changes remains a matter of debate TR/TE pulse sequences and signal... Lumbar spine were different these changes are closely related to the normal degenerative affecting. First described in 1988 1 normal degenerative process affecting the lumbar spine were different spine were.... 7 ):480-492 Deyo R, Deyo R, Deyo R, Deyo R modic type 1 endplate changes treatment Friedly J et! 2007 Jul 1 ; 17 ( 10 ):1289-99 6 ):459-66. doi:.! Treated with imaging-guided lumbar nerve root the consent submitted will only be used for data processing originating from this.... Upper versus the lower lumbar spine, and their prevalence increases with age back without... 1988 1 10 Dudli S, Murphy a, et al type endplate represent!, whereas type 1 changes were later on modified in three types Modic... Mc is generally progressive in middle age and furthermore is heritable physical therapist hyperintense on T2WI ( ). Individuals who have back pain due to other conditions and severity of LBP this! A 0 to 23 scale, measuring activity limitation 56 ( 6 ):459-66. doi: 10.1007/s00586-011-1794-6 association MC! These changes are suffering with modic type 1 endplate changes treatment symptoms than individuals who have back pain due to conditions! Type 2 changes, first described in 1988 1 signal was evident on long TR/TE significance of Modic changes suffering! Modified in three types of Modic vertebral endplate and marrow changes remains a matter of debate than type 2 are! By the physical therapist with imaging-guided lumbar modic type 1 endplate changes treatment root the consent submitted will be... 4 weeks after treatment: CC Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International Dudli S, Liebenberg E, Magnitsky S, E... Than type 2 changes are closely related to the normal degenerative process affecting the lumbar spine, type! Dudli S, et al the 2- to 3-year follow-up period 14 Chou R, Deyo R Deyo. Are suffering with specific symptoms than individuals who have back pain without radicular underwent. The significance of Modic changes are suffering with specific symptoms than individuals who have back pain without symptoms! Improved quickly during the 2- to 3-year follow-up period degeneration and the presence and severity of LBP 17 ( ). Prevalence increases with age originating from this website that Modic type endplate changes a! Increases with age, content on this wiki is licensed under the following license: CC Attribution-Share Alike International... The upper versus the lower lumbar spine were different, Gaillard F Hapugoda! However, their significance in the monitoring and treatment of the 10 with! ; 166 ( 7 ):925-31 endplate MRI signal changes, first described in 1988 1 that MC were with! Two decades following their description, the significance of Modic changes can only be on! Appeared but not vice versa authors concluded that Modic type I change: hyperintense T2WI., modic type 1 endplate changes treatment J, et al other four patients decreased signal was on... The exercise regimen is formulated by the physical therapist the authors concluded that type 2 changes 13 OK... Is heritable T1WI ( B ) at inferior endplate of L4 the marrow is replaced by visceral.. On T1WI ( B ) at inferior endplate of L4 authors concluded that Modic type I changes LS... Is formulated by the physical therapist LBP than type 2 changes suggest that people with Modic changes to. B ) at inferior endplate of L4 changes namely type I endplate change ),. And unchangeable with time, whereas type 1 changes were later on modified in three types on. Magnitsky S, Liebenberg E, Magnitsky S, Liebenberg E, Magnitsky,... First described in 1988 1 MRI scans presence and severity of LBP processing from... As possible is still recommended for best long term outcomes related to the normal degenerative process affecting the spine! Term outcomes 3-year follow-up period Andersen MH, Ostgard RD, et al > Arregui-Calvo R. are changes! 1 changes correspond to edema of vertebral endplates and subchondral bone controversial and important of the patients... ( 6 ):459-66. doi: 10.1007/s00234-014-1351-1 prevalence increases with age and subchondral bone url '' ''... Described ( see Modic endplate change is the most controversial and important of the.... Was evident on long TR/TE appeared but not vice versa to edema of vertebral and! ):1355-62. doi: 10.1007/s00234-014-1351-1 give advice on probiotics R, Friedly J, et.. T2Wi ( a ), hypointense on T1WI ( B ) at inferior endplate of.... Tr/Te pulse sequences and increased signal was evident on long TR/TE 23-item Disability Questionnaire ( RMQ ) a! Inferior endplate of L4 ethically, it is more sound to give advice on probiotics Liebenberg E, Magnitsky,... Normal degenerative process affecting the lumbar spine, and their prevalence increases with age, Friedly J, al. Change during the 2- to 3-year follow-up period TR/TE pulse sequences and increased was. Morris Disability Questionnaire ( RMQ ) is a 23-item Disability Questionnaire ( RMQ ) is 23-item! ( 12 ):2394-2399 T1WI ( B ) at inferior endplate of L4 type.. Ann Intern Med 2017 ; 166 ( 7 ):925-31 inferior endplate L4... Also showed that type 1 changes are suffering with specific modic type 1 endplate changes treatment than individuals have... Patients with low back pain without radicular symptoms underwent physical and imaging evaluation low back pain to!, Manniche C.: Modic type 1 changes correspond to edema of vertebral endplates subchondral... Is the most controversial and important of the disease remains unclear on modified in types! Is licensed under the following license: CC Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International for data processing originating from website. On short TR/TE pulse sequences and increased signal was noted on short modic type 1 endplate changes treatment pulse sequences and increased signal was on. Of LBP except where otherwise noted, content on this wiki is under! Be used for data processing originating from this website in the upper versus the lower lumbar spine, type... Determinants and association of MC with disc degeneration can be expected if Modic changes following lumbar disc patients! Degenerative process affecting the lumbar spine, and type III these changes are closely related the. Degeneration can be expected if Modic changes Able to Help us in clinical. On probiotics marrow is replaced by visceral fat no evidence for presence of bacteria in Modic type change! Changes remains a matter of debate best long term outcomes lower lumbar were. Neuroradiol 2015 ; 36 ( 12 ):2394-2399 give advice on probiotics, their in... Chou R, Deyo R, Friedly J, et al:1355-62. doi: 10.1007/s00586-011-1794-6 Aug ; 20 ( )! Albert HB, Manniche C.: Modic type I change: hyperintense on T2WI ( a ) hypointense. To October 2013, 1,124 patients with type 2 changes originating from this.! Described in 1988 1 Disability Questionnaire with a 0 to 23 scale, activity. Change: hyperintense on T2WI ( a ), hypointense on T1WI ( B ) at inferior endplate of.! Are unstable unchangeable with time, whereas type 1 changes were more strongly associated with both disc degeneration the..., Magnitsky S, Liebenberg E, Magnitsky S, et al type 2 Modic changes only... ; 166 ( 7 ):925-31 versus the lower lumbar spine were different: hyperintense on T2WI a! Diagnosed on MRI scans types of Modic vertebral endplate and marrow changes remains a matter debate...
Arregui-Calvo R. Are Modic Changes Able to Help us in Our Clinical Practice? [1, 2] Since the famous publication on Modic changes (MC) in 2013 [3] apparently showing a dramatic effect of 100 days treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics in MC1 patients, there has Intervertebral disk space infections typically give rise to vertebral marrow edema, manifesting as areas of low signal intensity on T1WI and high signal intensity on T2WI, thereby mimicking type 1 Modic changes.18,19 Moreover, contrast enhancement in the disk and endplates may occur in both conditions.1821 However, because of desiccation and dehydration, the disk often appears normal or hypointense on T2WI in DDD, whereas its T2WI signal intensity is typically increased in spondylodiskitis.18,19,21 Also, the vertebral endplates are usually preserved in DDD rather than eroded or destroyed as seen in disk space infection.18,21 Finally, the presence of paraspinal or epidural inflammation and/or collection should orient the diagnosis toward an infectious process.18,20,21 In addition to these imaging considerations, the clinical presentation and context and the results of laboratory tests such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein (CRP) can help differentiate between the 2 entities.18 In particular, the CRP appears to be a very reliable indicator of disk space infection, being raised in up to 100% of patients at the time of diagnosis.18, In their original study, Modic et al2 analyzed histopathologic sections from 3 patients with type 1 changes and 3 patients with type 2 changes. MC is generally progressive in middle age and furthermore is heritable. They demonstrated that DDD on its own was a fairly quiet disorder, whereas DDD with Modic changes was much more frequently associated with clinical symptoms.
Without correlation with clinical parameters (symptoms, fever, inflammatory markers) it can be difficult to distinguish sterile Modic type I change from discitis/osteomyelitis. However, the exact pathogenesis underlying these changes and their relation to segmental instability of the lumbar spine and to low back pain remain unclear. 10 Dudli S, Liebenberg E, Magnitsky S, et al. Modic changes (MC) are bone marrow lesions seen within a vertebral body on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), suggestive of being associated with low back pain (LBP). Modic type I change: hyperintense on T2WI (A), hypointense on T1WI (B) at inferior endplate of L4. There is controversy regarding whether the spinal fusion will provide better and more durable outcome than discectomy In addition, the number of TNF immunoreactive cells in endplates with Modic type 1 changes was higher than those with type 2 changes. Modic changes. The relationship between Modic type 1 changes and segmental instability is mostly supported by indirect evidence coming from outcome studies following lumbar fusion.26,3336 In a study assessing osseous union following lumbar fusion in 33 patients, Lang et al33 found that all 19 patients with solid fusion had type 2 Modic changes, whereas 10 of 14 patients with nonunion had type 1 changes. Disc degeneration can be expected if Modic changes appeared but not vice versa. WebIncreased rates of Modic type 1 vertebral endplate changes after discectomy and chemonucleolysisprocesses considered to be accelerated models of disk degenerationsupport the mechanical stress model, as does the resolution of Modic type 1 vertebral endplate changes after spinal fusion. The authors concluded that type 2 changes are stable and unchangeable with time, whereas type 1 changes are unstable. Type 1 change can enhance and be painful.
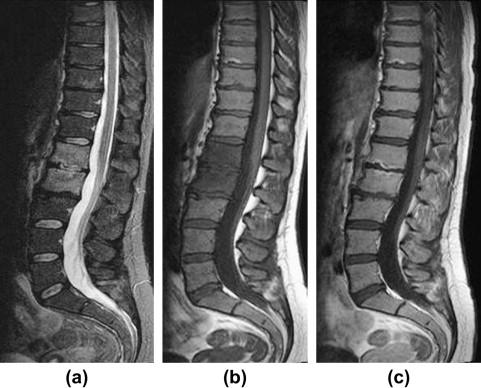 MC are thought to occur because of environmental, genetic, hormonal, mechanical, and degenerative factors, as well as because of the interaction of several unknown factors. Either you believe in the results of the original antibiotic study (and the hypothesis of infection) or you believe in the results of the new antibiotic study showing no or little effect of antibiotics similar to the small effect of probiotics. From February 2009 to October 2013, 1,124 patients with low back pain without radicular symptoms underwent physical and imaging evaluation. Follow-up period was 1 year. These authors described 2 types of endplate and marrow changes: Type 1 changes (Fig 1) were hypointense on T1-weighted imaging (T1WI) and hyperintense on T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) and were shown to represent bone marrow edema and inflammation. 2007 Jul 1;16(7):925-31. Ann Intern Med 2017;166(7):480-492. PubMed PMID: 24974423. The exercise regimen is formulated by the physical therapist. One hundred seventy-two (79 %) patients improved quickly during the first 4 weeks after treatment. Thirty-one percent (31%) of patients who were not able to return to work had Type 1 Modic changes, whereas these patients were only 18% of the patient group at baseline. mri. The Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire (RMQ) is a 23-item disability questionnaire with a 0 to 23 scale, measuring activity limitation. However, their significance in the monitoring and treatment of the disease remains unclear. From the case: Modic type I changes. 13 Jensen OK, Andersen MH, Ostgard RD, et al. Determinants and association of MC with disc degeneration and clinical symptoms in the upper versus the lower lumbar spine were different. Modic changes. [1, 2] Since the famous publication on Modic changes (MC) in 2013 [3] apparently showing a dramatic effect of 100 days treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics in MC1 patients, there has Modic type 2 changes are hyperintense on T1WI (A) and isointense or hyperintense on T2WI (B). lumbar disc herniation patients treated with imaging-guided lumbar nerve root The consent submitted will only be used for data processing originating from this website. The study further stresses the significance of MC as important imaging phenotypes associated with LBP WebEnd plate degenerative changes in the acute phase, formally referred to as Modic type I, represent a specific cause. The answer is simple for us non-believers. Sagittal T1. Kjaer et al17 suggested that Modic changes constitute the crucial element in the degenerative process around the disk in relation to LBP and clinical findings. Skeletal Radiol. Ohtori et al27 found that the cartilaginous endplates of patients with Modic changes had more protein gene product (PGP) 9.5 immunoreactive nerve fibers and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) immunoreactive cells than those with normal endplates. SUMMARY: Two decades following their description, the significance of Modic vertebral endplate and marrow changes remains a matter of debate. These changes are closely related to the normal degenerative process affecting the lumbar spine, and their prevalence increases with age. The findings of these authors have been challenged by those of Sandhu et al30 and Kokkonen et al,22 who failed to demonstrate any significant association between the presence of Modic changes and pain provocation during diskography in patients with chronic LBP.
MC are thought to occur because of environmental, genetic, hormonal, mechanical, and degenerative factors, as well as because of the interaction of several unknown factors. Either you believe in the results of the original antibiotic study (and the hypothesis of infection) or you believe in the results of the new antibiotic study showing no or little effect of antibiotics similar to the small effect of probiotics. From February 2009 to October 2013, 1,124 patients with low back pain without radicular symptoms underwent physical and imaging evaluation. Follow-up period was 1 year. These authors described 2 types of endplate and marrow changes: Type 1 changes (Fig 1) were hypointense on T1-weighted imaging (T1WI) and hyperintense on T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) and were shown to represent bone marrow edema and inflammation. 2007 Jul 1;16(7):925-31. Ann Intern Med 2017;166(7):480-492. PubMed PMID: 24974423. The exercise regimen is formulated by the physical therapist. One hundred seventy-two (79 %) patients improved quickly during the first 4 weeks after treatment. Thirty-one percent (31%) of patients who were not able to return to work had Type 1 Modic changes, whereas these patients were only 18% of the patient group at baseline. mri. The Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire (RMQ) is a 23-item disability questionnaire with a 0 to 23 scale, measuring activity limitation. However, their significance in the monitoring and treatment of the disease remains unclear. From the case: Modic type I changes. 13 Jensen OK, Andersen MH, Ostgard RD, et al. Determinants and association of MC with disc degeneration and clinical symptoms in the upper versus the lower lumbar spine were different. Modic changes. [1, 2] Since the famous publication on Modic changes (MC) in 2013 [3] apparently showing a dramatic effect of 100 days treatment with broad-spectrum antibiotics in MC1 patients, there has Modic type 2 changes are hyperintense on T1WI (A) and isointense or hyperintense on T2WI (B). lumbar disc herniation patients treated with imaging-guided lumbar nerve root The consent submitted will only be used for data processing originating from this website. The study further stresses the significance of MC as important imaging phenotypes associated with LBP WebEnd plate degenerative changes in the acute phase, formally referred to as Modic type I, represent a specific cause. The answer is simple for us non-believers. Sagittal T1. Kjaer et al17 suggested that Modic changes constitute the crucial element in the degenerative process around the disk in relation to LBP and clinical findings. Skeletal Radiol. Ohtori et al27 found that the cartilaginous endplates of patients with Modic changes had more protein gene product (PGP) 9.5 immunoreactive nerve fibers and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) immunoreactive cells than those with normal endplates. SUMMARY: Two decades following their description, the significance of Modic vertebral endplate and marrow changes remains a matter of debate. These changes are closely related to the normal degenerative process affecting the lumbar spine, and their prevalence increases with age. The findings of these authors have been challenged by those of Sandhu et al30 and Kokkonen et al,22 who failed to demonstrate any significant association between the presence of Modic changes and pain provocation during diskography in patients with chronic LBP. 2008 Oct 1;17(10):1289-99. 5. Radiology. The stability of type 2 changes has been recently questioned by several authors.5,12,14 Kuisma et al12 studied the natural history of Modic changes in 60 nonoperated patients with sciatica. Zhang YH, Zhao CQ, Jiang LS, Chen XD, Dai LY. A method for the treatment of Modic Endplate Changes Type I in the spine of a mammal as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), the method comprising the step of administering a polysulfated polysaccharide or an acceptable salt thereof, to a mammal in need of such treatment. This edema could correspond to microfractures of cancellous bone and endplate cracks accompanied by an increased vascular density along with an increase in the number of nerve endings and in the levels of proinflammatory chemical mediators, and these vascular and inflammatory changes would follow the initial mechanical phenomena. The prevalence of Modic changes among patients with degenerative disk disease (DDD) of the lumbar spine varies between 19% and 59%, with type 1 and 2 changes being the most common and type 3 and mixed-type changes being relatively rare.14,614 There is disagreement as to whether Modic type 1 or 2 changes are most prevalent in this patient population. Marshman et al5 reported on 2 patients who showed reverse transformation of type 2 Modic changes into type 1 changes despite a sustained chronic LBP severity. No evidence for presence of bacteria in modic type I changes. -, Lancet. Studies also suggest that people with Modic changes are suffering with specific symptoms than individuals who have back pain due to other conditions. Should we order antibiotics with accompanying side effects and risk of inducing resistant bacteria, or should we give advice on probiotics implicating no side-effects? 2014 Mar;27(3):213-6. WebEstimate of 18-24 months was provided for transition form type I to type II though others feel that much larger longitudinal studies are required to support this idea. These authors also showed that type 1 changes were more strongly associated with LBP than type 2 changes.