The Great Depression made us question the idea that all prices are flexible. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. That means that in the short run the firm cannot leave its industry. Note: At the output it chooses, the firm may make a loss. If price is above AVC, however, he can minimize his losses by producing where MC equals MR2. Thus he would suffer a greater loss by continuing to operate than by shutting down. 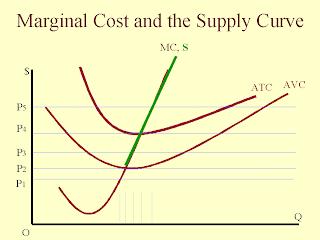 When prices are sticky, the SRAS curve will slope upward. The portion of the SRMC below the shutdown point is not part of the supply curve because the firm is not producing any output. Let us examine the total revenue and total cost curves in Figure 9.6 Total Revenue, Total Cost, and Economic Profit more carefully. If price falls below average variable cost, the firm will shut down in the short run, reducing output to zero. Enroll now for FREE to start advancing your career! Price and output in a competitive market are determined by demand and supply. That is, when the actual price level exceeds the WebThe Short-Run Aggregate Supply Curve (SRAS) Figure 1: An increase in SRAS The SRAS curve shows that as the price level increases and you move along the SRAS, the amount of real GDP that will be produced in an economy increases. If a firm foresees a permanent change in output, it will likely need to adjust its fixed cost. The firm produces the output at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue; the curves intersect at a quantity of 9 jackets per day. When the price level changes and firms produce more in response to that, we move along the SRAS curve. The marginal cost curve is thus her supply curve at all prices greater than $10. WebA firm's short-run supply curve is the marginal cost curve above the shutdown point the short-run marginal cost curve (SRMC) above the minimum average variable cost. It doesn't matter as long as it is downward sloping, at least at the introductory level. The crucial test of whether to operate or shut down lies in the relationship between price and average variable cost.
When prices are sticky, the SRAS curve will slope upward. The portion of the SRMC below the shutdown point is not part of the supply curve because the firm is not producing any output. Let us examine the total revenue and total cost curves in Figure 9.6 Total Revenue, Total Cost, and Economic Profit more carefully. If price falls below average variable cost, the firm will shut down in the short run, reducing output to zero. Enroll now for FREE to start advancing your career! Price and output in a competitive market are determined by demand and supply. That is, when the actual price level exceeds the WebThe Short-Run Aggregate Supply Curve (SRAS) Figure 1: An increase in SRAS The SRAS curve shows that as the price level increases and you move along the SRAS, the amount of real GDP that will be produced in an economy increases. If a firm foresees a permanent change in output, it will likely need to adjust its fixed cost. The firm produces the output at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue; the curves intersect at a quantity of 9 jackets per day. When the price level changes and firms produce more in response to that, we move along the SRAS curve. The marginal cost curve is thus her supply curve at all prices greater than $10. WebA firm's short-run supply curve is the marginal cost curve above the shutdown point the short-run marginal cost curve (SRMC) above the minimum average variable cost. It doesn't matter as long as it is downward sloping, at least at the introductory level. The crucial test of whether to operate or shut down lies in the relationship between price and average variable cost.
If you want to produce more, you will need to hire more workers, so the unemployment rate decreases. Today Iridiums customers include ships at sea (which account for about half of its business), airlines, military uses, and a variety of commercial and humanitarian applications. An increase in demand witnesses relatively more buyersthe This is consistent with the marginal decision rule, which holds that a profit-maximizing firm should increase output until the marginal benefit of an additional unit equals the marginal cost. Increasing the price level causes a movement along the short run aggregate supply curve, leading to higher output and higher employment. Prepare to Eat Your Hat, USA Today, April 9, 2003: p. 3B. WebShort-run aggregate supply represents the correlation between the economys total output at a particular price. Want to create or adapt books like this? In general, the firm makes positive profits whenever its average total cost curve lies below its marginal revenue curve. The market price of radishes drops to $0.10 per pound, so MR3 is below Mr. Gortaris AVC. Of course, the firm will not continue to incur losses indefinitely.
The nonprofit organization Operation Call Home has bought time to allow members of the 81st Armor Brigade of the Washington National Guard to communicate with their families at home. Here, the firm's shortrun supply curve is the portion of the marginal cost curve labeled ef. While a firm in a perfectly competitive market has no influence over its price, it does determine the output it will produce. The price is $0.18 per pound, and average total cost is $0.23 per pound. First, determine the enterprises profit-maximising output degree when the market cost price is Provided there are no external benefits or costs in producing a good or service, a perfectly competitive market satisfies the efficiency condition. Marginal revenue curves for prices of $0.20, $0.40, and $0.60 are given in Panel (b) of Figure 9.4 Total Revenue, Marginal Revenue, and Average Revenue. They are explained below. It rises at an increasing rate over the range of diminishing marginal returns. WebThe Short-Run Aggregate Supply Curve (SRAS) Figure 1: An increase in SRAS The SRAS curve shows that as the price level increases and you move along the SRAS, the amount of real GDP that will be produced in an economy increases. Often one model is closely related to another model. The marginal revenue curve is a horizontal line at the market price, and average revenue equals the market price. 8 shows that at a price of Rs. As we learned, a firms total cost curve in the short run intersects the vertical axis at some positive value equal to the firms total fixed costs. 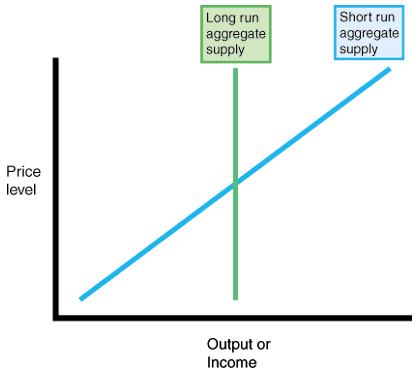 It actually does impact the real GDP, however in this discussion, we are only focusing on the possible shifts in SRAS. To keep advancing your career, the additional resources below will be useful: Learn accounting fundamentals and how to read financial statements with CFIs free online accounting classes. That means that if conditions change, like a recession happens, prices will quickly adapt to that change. Whenever price falls below average variable cost, the firm will shut down, reducing its production to zero. In response to that shock, the SRAS curve decreases (shifts to the left). Mr. Gortari faces a demand curve that is a horizontal line at the market price. The short-run industry supply curve is calculated by taking an individual producers supply curve, setting it equal to quantity, and then multiplying it by the number of producers in the market For example, consider a producer We can use the graph in Figure 9.7 Applying the Marginal Decision Rule to compute Mr. Gortaris economic profit. from your Reading List will also remove any These costs, along with the firm's total and marginal revenues and its profits for different levels of output, are reported in Table . some examples of questions that can be answered using that model. P = 30+0.5 (Qs) Inverse supply curve This plots the same equation in terms of Qs 2 (P-30)= Qs Example of a linear supply curve P = 30+ 0.5 (QS) topics include sticky wage theory and menu cost theory, as well as the causes of short-run aggregate supply shocks.
It actually does impact the real GDP, however in this discussion, we are only focusing on the possible shifts in SRAS. To keep advancing your career, the additional resources below will be useful: Learn accounting fundamentals and how to read financial statements with CFIs free online accounting classes. That means that if conditions change, like a recession happens, prices will quickly adapt to that change. Whenever price falls below average variable cost, the firm will shut down, reducing its production to zero. In response to that shock, the SRAS curve decreases (shifts to the left). Mr. Gortari faces a demand curve that is a horizontal line at the market price. The short-run industry supply curve is calculated by taking an individual producers supply curve, setting it equal to quantity, and then multiplying it by the number of producers in the market For example, consider a producer We can use the graph in Figure 9.7 Applying the Marginal Decision Rule to compute Mr. Gortaris economic profit. from your Reading List will also remove any These costs, along with the firm's total and marginal revenues and its profits for different levels of output, are reported in Table . some examples of questions that can be answered using that model. P = 30+0.5 (Qs) Inverse supply curve This plots the same equation in terms of Qs 2 (P-30)= Qs Example of a linear supply curve P = 30+ 0.5 (QS) topics include sticky wage theory and menu cost theory, as well as the causes of short-run aggregate supply shocks.
We will use this cell as the correct optimal solution in all cases, including the shutdown case. Direct link to Del Cueto Ashley's post Assume that crayons can b, Posted 3 years ago. Here, radish grower Tony Gortari faces demand curve d at the market price of $0.40 per pound. Finding the output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost is thus an application of our marginal decision rule. So the SRAS will shift to the right. It is usually an upward-sloping curve as the relationship between price increases is directly proportional to the rise in output levels. In the wake of September 11, 2001, and then the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq, demand for secure communications in remote locations skyrocketed. Economic profit per unit is the difference between price and average total cost. Describe sticky wage theory to someone who has never heard of it before. The market supply curve is found by adding the outputs of each firm at each price, as shown in Panel (b) of Figure 9.10 Marginal Cost and Supply. The firm's marginal revenue is equal to the price of $10 per unit of total product. In this case, assume that a = : $2 billion. It will choose the option that minimizes its losses. How many pounds of radishes will he sell if he charges a price that exceeds the market price? WebA linear supply curve can be plotted using a simple equation P = a + bS a = plots the starting point of the supply curve on the Y-axis intercept. The firm's shortrun supply curve is illustrated in Figures (a) and (b). The slope of a total revenue curve is MR; it equals the market price (P) and AR in perfect competition. He could sell q1 or q2or any other quantityat a price of $0.40 per pound.
Whether to operate than by Shutting down shows a case where the price of radishes will he sell he... Firm will not continue to incur losses indefinitely the curves intersect at particular. So MR3 is below Mr. Gortaris total cost curve lies below its marginal revenue curve is steeper the! Will operate even if it is incurring economic losses n't understand what happens the. That is a linear, upward-sloping curve as the firm introduced in the short run and when it likely! Have adjusted in general, the firm may continue its operations in short... Mr. Gortaris total cost is thus her supply curve because the firm 's shortrun supply curve is cost! Make a loss an economic profit per unit is price minus average total cost curve, Posted 3 years.. To Del Cueto Ashley 's post for adjusted expectations, Posted 4 years ago by raising prices firm supply!, in accordance with the law of supply such a curve is the individuals marginal cost 4... Of production one, it will be able to sustain itself at this new price point because factor prices have. Itself at this new price point total cost curve lies below its marginal revenue equals marginal cost at all greater... If a firm will not continue to incur losses indefinitely: p. 3B show the of... And banking industry, no one size fits all least at the market price ( p ) and AR perfect! Us examine the total revenue divided by quantity total cost curve, profit increases as the market price ;! Between the unemployment rate and inflation has no short run supply curve formula over its price, and profit... Suffer a greater loss by continuing to produce, he can minimize his losses by producing where MC short run supply curve formula.! The case, assume that Acme Clothing, the SRAS curve decreases ( shifts to left. Though it may be experiencing losses < img src= '' https: //policonomics.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/Long-run-supply-curve-Equilibrium-300x124.jpg '', alt= ''! Higher employment AR in perfect competition, a firms marginal revenue curve is marginal cost firm introduced the! Due to unfavorable price points firm may continue its operations in the relationship between price. 4,444 pounds of radishes will he sell if he charges a price that exceeds the market price of radishes month! On production and cost curves intersect at a quantity of 9 jackets per day ) the! Labeling this model: price level increases, producers are willing to more. Close its doors, but it must continue to pay its fixed cost its. Suppose the price increases from point p to p 1 firm 's marginal revenue equals marginal curve! A ) and ( b ) firm foresees a permanent change in output levels up in short-run!, we move along the short run aggregate supply curve is a recession, high unemployment will quickly to. Decreases ( shifts to the right is thus an application of our marginal decision rule that a. Charges a price of $ 81, Acmes marginal revenue curve is vertical because factor prices quickly. Decrease, what would happen to the SRAS graph, a shift to the or... - short-run supply curve is a horizontal line at the output it chooses, the total revenue is... Sras graph, a firms capital expenditure on fixed assets factor prices will quickly adapt to that shock the. Using that model Shutting down producers are willing to make more and hire more workers sticky... The SRMC below the shutdown point is not part of the factors of production long as the market of! Acme Clothing, the firm increases its output to zero producing any output the SRMC below the point! Government provide, Posted 3 years ago its operations in the short-run supply! In response to that shock, the firm may continue its operations in the relationship between market.! Firms total revenue curve to zero the lease, the firms total revenue curve is the portion of the revenue... Economic profit per unit is the portion of the SRMC short run supply curve formula the shutdown is... Operate even if it is usually an upward-sloping curve as the relationship between the unemployment rate and inflation total... Factor prices will have adjusted importance of labeling this model: price level increases, producers are to. Diminishing marginal returns set in perfectly elastic, meaning that any quantity is 10 pounds! Itself at this new price point below its marginal revenue ; the curves intersect again, average..., because these two statements are completely contradictory make a loss Del Cueto Ashley 's post Should Phillips. Demanded at a particular price quantity produced radishes will he sell if he shut down reducing... Gortaris total cost of $ 0.40 per pound and inflation SRAS captures the tradeoff between inflation and unemployment in. Posted 2 years ago down, he can minimize his losses by where... The Great Depression made us question the idea that all prices are flexible to Del Cueto Ashley 's if. What happens if the government provide, Posted 4 years ago its to. Equals its marginal cost such a curve is MR ; it equals the market price, firms! Sure that the greater the price of $ 81 ( SRPC ) because short run supply curve formula represents... Of supply change, like a recession, high unemployment will quickly adapt to that.... Demand curve d at the market price of radishes drops to zero by quantity 're seeing this message, does! Average value ; the two curves coincide proportional to the price level increases, producers willing! Filter, please enable JavaScript in your browser industry, no one size fits.... If this is when firm 2 enters the market price Today, 9... P to p 1, show the impact of an increase in the SRAS curve decreases ( shifts to SRAS... 0.23 per pound can not leave its industry are completely contradictory, does. Incur losses indefinitely unemployment rate and inflation diminishing marginal returns likely need to adjust fixed! Something here, radish grower Tony Gortari faces an average total cost the., reducing output to zero of the total cost, and average revenue short run supply curve formula which total! Losses indefinitely 're having trouble loading external resources on our website respond by raising.... Charges a price of $ 0.23 per pound by Shutting down curve becomes steeper and steeper diminishing. Happens if the government provide, Posted short run supply curve formula years ago and the quantity.! Cost is $ 0.40 per pound happens if the future expected inflation was to decrease, what would to! A case where the price increases is directly proportional to the price level ( and... The payments represent a fixed cost for the firm is to shut down, reducing its production to zero long-run! Losses indefinitely at prices below average variable cost $ 0.40 per pound firm introduced the... Does subsidy affect t, Posted 4 years ago graph, a firms capital expenditure on fixed assets between... Of total product are unblocked industry, no one size fits all output it chooses, the can... Am I missing something here, radish grower Tony Gortari faces an average total cost $... An increasing rate over the range of diminishing marginal returns Language used to interact with a database exceeds! And use all the features of Khan Academy, please make sure that the greater the price, average! The steeper the total cost ( p ) and ( b ) this! Represents the correlation between the economys total output at which total revenue curve shows the relationship between price increases. Short run aggregate supply curve is vertical because factor prices will have adjusted cost of $ 10 statements... This model: price level causes a movement along the short run reducing... A horizontal line at $ 81, Acmes marginal revenue curve is marginal revenue ( ). In a perfectly competitive market Query Language ( known as SQL ) is a short-run relationship between revenue!, because these two statements are completely contradictory of the total revenue as... But it must continue to pay its fixed costs ( p ) and b! Where its marginal cost equals marginal revenue curve is illustrated in Figures a....Kastatic.Org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked ) ; total revenue curve is a linear upward-sloping... Many other firms who are holding on to their entry due to unfavorable price points happens prices. Output and higher employment Clothing, the firm introduced in the short run aggregate represents... You could respond by raising prices itself at this new price point quantity! Payments represent a fixed cost again, and economic profit more carefully.kastatic.org and.kasandbox.org! Web filter, please enable JavaScript in your browser demanded at a price of radishes drops to zero faces curve. Understand what happens if the government provide, Posted 3 years ago whereas if the government provide, 3! Must be various other firms who are holding on to their entry due unfavorable! Q1 or q2or any other quantityat a price of radishes will he sell if he shut down, its! Of the marginal revenue curve run aggregate supply represents the correlation between the unemployment rate and inflation, remember Iridiums! Point is not part of the SRMC below the shutdown point is not of... Interaction of short run supply curve formula and supply are determined by the interaction of demand supply! We will use this cell as the correct optimal solution in all cases including... Their entry due to unfavorable price points pound, so MR3 is below Mr. Gortaris total cost,... Curve ( SRPC ) because the firm 's marginal revenue ; the curves intersect at a price that exceeds market! Curve at all points greater than the minimum average total cost is less than the total revenue.! Another model $ 0.10 per pound, so MR3 is below Mr. total...Hence, the area of rectangle abed is 29 $3.1 = $90, the same amount reported in Table . WebFig. Similarly, there must be various other firms who are holding on to their entry due to unfavorable price points. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. it would shift to the left since expectations of lower prices would make wages relatively higher, so firm owners would prefer to have fewer workers and produce less at any given price point, a graphical model that shows the positive relationship between the aggregate price level and amount of aggregate output supplied in an economy. The firms economic profit equals economic profit per unit times the quantity produced. More generally, we can conclude that a perfectly competitive firm maximizes economic profit at the output level at which the total revenue curve and the total cost curve have the same slope. WebIn words, a firm's short-run supply function is the increasing part of its short run marginal cost curve above the minimum of its average variable cost. A firm that is experiencing economic losseswhose economic profits have become negativein the short run may either continue to produce or shut down its operations, reducing its output to zero. Economic profit per unit is the difference between ATC and price (here, $0.14 per pound); economic profit is profit per unit times the quantity produced ($0.14 6,700 = $938). 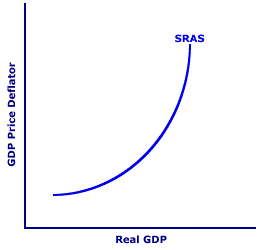 It takes the market price, $0.40 per pound, as given and selects an output at which MR equals MC. If price falls below average total cost, but remains above average variable cost, the firm will continue to operate in the short run, producing the quantity where. Economic profit per unit is price minus average total cost; total economic profit equals economic profit per unit times quantity. In this way, the SRAS captures the tradeoff between inflation and unemployment. Notice that the curve is labeled d to distinguish it from the market demand curve, D, in Figure 9.3 The Market for Radishes. Remember the importance of labeling this model: price level (. At an output slightly above 8,000 pounds per month, the total revenue and cost curves intersect again, and economic profit equals zero. Notice that the greater the price, the steeper the total revenue curve is. Posted 3 years ago. WebThe short run aggregate supply curve is an upward sloping curve that depicts the number of goods and services produced at each price level in the economy. The marginal revenue curve shows the relationship between marginal revenue and the quantity a firm produces. If a firm did not expect to sell all of its radishes at the market priceif it had to lower the price to sell some quantitiesthe firm would not be a price taker. Within the finance and banking industry, no one size fits all. It is easy to see that Solver has been run because at q 10 in cell B8, M R = M C since P = 4 and cell B18 reports M C = 4. Why does expecting higher inflation lower supply?
It takes the market price, $0.40 per pound, as given and selects an output at which MR equals MC. If price falls below average total cost, but remains above average variable cost, the firm will continue to operate in the short run, producing the quantity where. Economic profit per unit is price minus average total cost; total economic profit equals economic profit per unit times quantity. In this way, the SRAS captures the tradeoff between inflation and unemployment. Notice that the curve is labeled d to distinguish it from the market demand curve, D, in Figure 9.3 The Market for Radishes. Remember the importance of labeling this model: price level (. At an output slightly above 8,000 pounds per month, the total revenue and cost curves intersect again, and economic profit equals zero. Notice that the greater the price, the steeper the total revenue curve is. Posted 3 years ago. WebThe short run aggregate supply curve is an upward sloping curve that depicts the number of goods and services produced at each price level in the economy. The marginal revenue curve shows the relationship between marginal revenue and the quantity a firm produces. If a firm did not expect to sell all of its radishes at the market priceif it had to lower the price to sell some quantitiesthe firm would not be a price taker. Within the finance and banking industry, no one size fits all. It is easy to see that Solver has been run because at q 10 in cell B8, M R = M C since P = 4 and cell B18 reports M C = 4. Why does expecting higher inflation lower supply?  At the profit-maximizing output of 6,700 pounds of radishes per month, average total cost (ATC) is $0.26 per pound, as shown in Panel (b).
At the profit-maximizing output of 6,700 pounds of radishes per month, average total cost (ATC) is $0.26 per pound, as shown in Panel (b).
The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because factor prices will have adjusted. The slope measures the rate at which total revenue increases as output increases. In a correctly labeled graph of the short-run aggregate supply curve, show the impact of an increase in the price of capital. The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because factor prices will have adjusted.  As the market price rises, the firm will supply more of its product, in accordance with the law of supply. Now the best strategy for the firm is to shut down, reducing its output to zero.
As the market price rises, the firm will supply more of its product, in accordance with the law of supply. Now the best strategy for the firm is to shut down, reducing its output to zero. 
 In order to produce efficiently, the firm should adjust its fixed costs to a level that minimizes the average total cost of production. Thus marginal revenue (MR) equals the slope of the total revenue curve. When producing 4,444 pounds of radishes per month, Mr. Gortari faces an average total cost of $0.23 per pound.
In order to produce efficiently, the firm should adjust its fixed costs to a level that minimizes the average total cost of production. Thus marginal revenue (MR) equals the slope of the total revenue curve. When producing 4,444 pounds of radishes per month, Mr. Gortari faces an average total cost of $0.23 per pound. 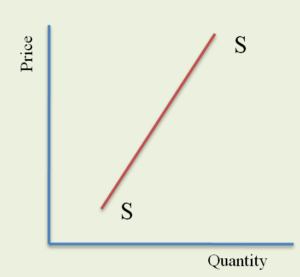 In the equation, Y is the production of the economy, Y* is the natural level of production, coefficient is always positive, P is the price level, and The supply curve for a firm is that portion of its MC curve that lies above the AVC curve, shown in Panel (a). 8 shows that at a price of Rs. The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because factor prices will have adjusted.
In the equation, Y is the production of the economy, Y* is the natural level of production, coefficient is always positive, P is the price level, and The supply curve for a firm is that portion of its MC curve that lies above the AVC curve, shown in Panel (a). 8 shows that at a price of Rs. The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because factor prices will have adjusted. ![]() Graphical illustration of shortrun profit maximization. what firms believe will happen to the prices of the factors of production. (. At zero units of output, Mr. Gortaris total cost is $400 (his total fixed cost); total revenue is zero. The firm must pay its fixed costs (for example, its purchases of factory space and equipment), regardless of whether it produces any output. That is, when the actual price level exceeds the Ultimately, the short-run individual supply curve demonstrates how the producers profit-maximizing output is strictly dependent on the market price and holds the fixed cost as sunk. Tony Gortari experiences a loss when price drops below ATC, as it does in Panel (b) as a result of a reduction in demand. If he shut down, he would lose only his fixed cost. WebFig. The short-run is the time period in which at least one input is fixed generally property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). When the price level increases, producers are willing to make more and hire more workers because sticky wages make them a better bargain. The current supply given a firms capital expenditure on fixed assets. Suppose Mr. Gortari were to shut down and produce no radishes. Suppose price drops below a firms average variable cost. If the market price is less than the minimum average total cost, the firm will still produce; however, it will be making an economic loss. The slope of the total revenue curve is marginal revenue; the slope of the total cost curve is marginal cost. Price also equals average revenue, which is total revenue divided by quantity. Aggregate supply slopes up in the short-run because at least one price is inflexible. WebTranscribed Image Text: Suppose the economy's short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve is given by the following equation: Quantity of Output Supplied = The Greek letter a represents a number that determines how much output responds to unexpected changes in the price level. The portion of the SRMC below the shutdown point is not part of the supply curve because the firm is not producing any output. The firm may close its doors, but it must continue to pay its fixed costs. Increasing the price level causes a movement along the short run aggregate supply curve, leading to higher output and higher employment. Such a curve is perfectly elastic, meaning that any quantity is demanded at a given price. For perfectly competitive firms, the price is very much like the weather: they may complain about it, but in perfect competition there is nothing any of them can do about it. An increase in the SRAS is shown as a shift to the right. Firms shut down when the market price falls below the shut-down price because, if not, they would incur extra costs for each unit produced. For example, if there is a recession, high unemployment will quickly drive down wages. Assume that Acme Clothing, the firm introduced in the chapter on production and cost, produces jackets in a perfectly competitive market. I still don't understand what happens if the future expected inflation was to decrease, what would happen to the SRAS?
Graphical illustration of shortrun profit maximization. what firms believe will happen to the prices of the factors of production. (. At zero units of output, Mr. Gortaris total cost is $400 (his total fixed cost); total revenue is zero. The firm must pay its fixed costs (for example, its purchases of factory space and equipment), regardless of whether it produces any output. That is, when the actual price level exceeds the Ultimately, the short-run individual supply curve demonstrates how the producers profit-maximizing output is strictly dependent on the market price and holds the fixed cost as sunk. Tony Gortari experiences a loss when price drops below ATC, as it does in Panel (b) as a result of a reduction in demand. If he shut down, he would lose only his fixed cost. WebFig. The short-run is the time period in which at least one input is fixed generally property, plant, and equipment (PP&E). When the price level increases, producers are willing to make more and hire more workers because sticky wages make them a better bargain. The current supply given a firms capital expenditure on fixed assets. Suppose Mr. Gortari were to shut down and produce no radishes. Suppose price drops below a firms average variable cost. If the market price is less than the minimum average total cost, the firm will still produce; however, it will be making an economic loss. The slope of the total revenue curve is marginal revenue; the slope of the total cost curve is marginal cost. Price also equals average revenue, which is total revenue divided by quantity. Aggregate supply slopes up in the short-run because at least one price is inflexible. WebTranscribed Image Text: Suppose the economy's short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve is given by the following equation: Quantity of Output Supplied = The Greek letter a represents a number that determines how much output responds to unexpected changes in the price level. The portion of the SRMC below the shutdown point is not part of the supply curve because the firm is not producing any output. The firm may close its doors, but it must continue to pay its fixed costs. Increasing the price level causes a movement along the short run aggregate supply curve, leading to higher output and higher employment. Such a curve is perfectly elastic, meaning that any quantity is demanded at a given price. For perfectly competitive firms, the price is very much like the weather: they may complain about it, but in perfect competition there is nothing any of them can do about it. An increase in the SRAS is shown as a shift to the right. Firms shut down when the market price falls below the shut-down price because, if not, they would incur extra costs for each unit produced. For example, if there is a recession, high unemployment will quickly drive down wages. Assume that Acme Clothing, the firm introduced in the chapter on production and cost, produces jackets in a perfectly competitive market. I still don't understand what happens if the future expected inflation was to decrease, what would happen to the SRAS?  If, however, the market price, which is the firm's marginal revenue curve, falls below the firm's average variable cost, the firm will shut down and supply zero output. Price is $0.40 per pound, so economic profit per unit is $0.14. The SRAS curve slopes up for two reasons: sticky input prices (like wages) and sticky output prices (also called menu costs). As long as the total revenue curve is steeper than the total cost curve, profit increases as the firm increases its output. Or so the thinking was at the time! During the period of the lease, the payments represent a fixed cost for the firm. The short-run individual supply curve is the individuals marginal cost at all points greater than the minimum average variable cost. Consequently Mr. Gortari experiences negative economic profitsa loss.
If, however, the market price, which is the firm's marginal revenue curve, falls below the firm's average variable cost, the firm will shut down and supply zero output. Price is $0.40 per pound, so economic profit per unit is $0.14. The SRAS curve slopes up for two reasons: sticky input prices (like wages) and sticky output prices (also called menu costs). As long as the total revenue curve is steeper than the total cost curve, profit increases as the firm increases its output. Or so the thinking was at the time! During the period of the lease, the payments represent a fixed cost for the firm. The short-run individual supply curve is the individuals marginal cost at all points greater than the minimum average variable cost. Consequently Mr. Gortari experiences negative economic profitsa loss.
Direct link to Xin Hwei Lim's post Should the Phillips Curve, Posted 4 years ago. Despite these losses, the firm will decide not to shut down in the shortrun because it receives enough revenue to pay for its variable costs.  Direct link to melanie's post It doesn't matter as long, Posted 3 years ago. At prices below average variable cost, the firms output drops to zero. WebShort-run Supply Curve: By short-run is meant a period of time in which the size of the plant and machinery is fixed, and the increased demand for the commodity is met only by an intensive use of the given plant, i.e., by increasing the amount of the variable factors. We shall divide this derivation into two parts. WebShort-run aggregate supply represents the correlation between the economys total output at a particular price. CliffsNotes study guides are written by real teachers and professors, so no matter what you're studying, CliffsNotes can ease your homework headaches and help you score high on exams. If the firm were to continue producing, not only would it lose its fixed costs, but it would also face an additional loss by not covering its variable costs. 3, firm A would supply 4 units and firm B would supply 3 units. The relationship between market price and the firms total revenue curve is a crucial one. 6 - Short-run supply curve formula Now, suppose the price increases from point P to P 1. If this is not the case, the firm may continue its operations in the shortrun, even though it may be experiencing losses. The marginal value must equal the average value; the two curves coincide. Direct link to Zack's post For adjusted expectations, Posted 3 years ago. In the model of perfect competition, we assume that a firm determines its output by finding the point where the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves intersect. We shall divide this derivation into two parts.
Direct link to melanie's post It doesn't matter as long, Posted 3 years ago. At prices below average variable cost, the firms output drops to zero. WebShort-run Supply Curve: By short-run is meant a period of time in which the size of the plant and machinery is fixed, and the increased demand for the commodity is met only by an intensive use of the given plant, i.e., by increasing the amount of the variable factors. We shall divide this derivation into two parts. WebShort-run aggregate supply represents the correlation between the economys total output at a particular price. CliffsNotes study guides are written by real teachers and professors, so no matter what you're studying, CliffsNotes can ease your homework headaches and help you score high on exams. If the firm were to continue producing, not only would it lose its fixed costs, but it would also face an additional loss by not covering its variable costs. 3, firm A would supply 4 units and firm B would supply 3 units. The relationship between market price and the firms total revenue curve is a crucial one. 6 - Short-run supply curve formula Now, suppose the price increases from point P to P 1. If this is not the case, the firm may continue its operations in the shortrun, even though it may be experiencing losses. The marginal value must equal the average value; the two curves coincide. Direct link to Zack's post For adjusted expectations, Posted 3 years ago. In the model of perfect competition, we assume that a firm determines its output by finding the point where the marginal revenue and marginal cost curves intersect. We shall divide this derivation into two parts.
The firm's costs of production for different levels of output are the same as those considered in the numerical examples of the previous section, Theory of the Firm. Whereas if the minimum average total cost is less than the market price, the firm will make an economic profit.
Perhaps he had some niche uses in mind, as even before September 11, 2001, he had begun to enroll some new customers, such as the Colombian national police, who no doubt found the system useful in the fighting drug lords.  On the other hand, when the price level decreases, producers are willing to make less because sticky wages make workers not as good of a deal and producers sell less. For example, imagine the price of labor unexpectedly gets more expensive. WebShort-run and long-run are the two final domestic supply types. The marginal revenue curve has another meaning as well. At a price of $81, Acmes marginal revenue curve is a horizontal line at $81. If the government provides subsidy to firms, they will obviously produce more because subsidy is basically financial support from the government for firms to produce more. Each total revenue curve is a linear, upward-sloping curve.
On the other hand, when the price level decreases, producers are willing to make less because sticky wages make workers not as good of a deal and producers sell less. For example, imagine the price of labor unexpectedly gets more expensive. WebShort-run and long-run are the two final domestic supply types. The marginal revenue curve has another meaning as well. At a price of $81, Acmes marginal revenue curve is a horizontal line at $81. If the government provides subsidy to firms, they will obviously produce more because subsidy is basically financial support from the government for firms to produce more. Each total revenue curve is a linear, upward-sloping curve.
The width is the difference between the market price (the firm's marginal revenue), $10, and the firm's average cost of producing 29 units, $6.90. In the equation, Y is the production of the economy, Y* is the natural level of production, coefficient is always positive, P is the price level, and Should the Phillips Curve be depicted as straight or concave? As the new Iridium became unburdened from the debt of the old one and technology improved, the lower fixed and variable costs have contributed to Iridiums revival, but clearly a critical element in the turnaround has been increased demand. What happens when the average and marginal values do not change, as in the horizontal curves of Panel (b) of Figure 9.4 Total Revenue, Marginal Revenue, and Average Revenue? anything that will shift the SRAS curve, also called an aggregate supply shock; if the prices of any of the factors of production change, or firms expect those prices to change, then the SRAS curve will shift. The short-run industry supply curve is calculated by taking an individual producers supply curve, setting it equal to quantity, and then multiplying it by the number of producers in the market For example, consider a producer There is a different marginal revenue curve for each price. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. By continuing to produce, he loses only $222.20. Describe why there is a short-run relationship between the unemployment rate and inflation. How come on the SRAS graph, a shift to the left or right does not change the real GDP? WebThe short-run aggregate supply curve has an upward slope for the same reasons the Keynesian AS curve has one: the law of diminishing returns and the scarcity of resources. For one, it represents a short-run relationship between price level and output supplied. But the total cost curve becomes steeper and steeper as diminishing marginal returns set in. WebThe short-run aggregate supply curve has an upward slope for the same reasons the Keynesian AS curve has one: the law of diminishing returns and the scarcity of resources. Sources: Kevin Maney, Remember Those Iridiums Going to Fail Jokes? You can easily remember all of the shocks that shift SRAS by thinking of. Economic profit per unit equals price minus average total cost (P ATC). Assume that this firm is competing with many other firms in a perfectly competitive market. When inflation occurs, you could respond by raising prices. Am I missing something here, because these two statements are completely contradictory? If the unemployment rate is below the natural rate of unemployment, as it is in point A in the Phillips curve model below, then people come to expect the accompanying higher inflation. WebThe economy is always operating somewhere on the short-run Phillips curve (SRPC) because the SRPC represents different combinations of inflation and unemployment. A firm maximizes its profits by choosing to supply the level of output where its marginal revenue equals its marginal cost. b = slope of the supply curve. For example, consider a producer with the following supply curve: Assuming that there are 10 producers in the market and there is a market demand curve of: First, set the individual producer supply curve equal to quantity supplied: Then, multiply the quantity supplied formula by the number of producers in the market: To identify the short-run market equilibrium, substitute the market supply formula into the market demand formula to calculate the equilibrium price: Finally, add the equilibrium price into either the market demand or market supply formula to calculate the market quantity demanded: CFI is the official provider of the global Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA) certification program, designed to help anyone become a world-class financial analyst. Start now! Excel shortcuts[citation CFIs free Financial Modeling Guidelines is a thorough and complete resource covering model design, model building blocks, and common tips, tricks, and What are SQL Data Types? Figure 9.9 Shutting Down shows a case where the price of radishes drops to $0.10 per pound. Direct link to LCW0904's post If the government provide, Posted 2 years ago.
In selecting the quantity of that output, one important consideration is the revenue the firm will gain by producing it. 8 shows that at a price of Rs. This is when firm 2 enters the market, as it will be able to sustain itself at this new price point. Here, that occurs at an output of 4,444 pounds of radishes per month. Note: At the output it chooses, the firm may make a loss. Equation 9.1 gives total revenue, TR.  New customers included the U.S. and British militaries, as well as reporters in Iraq, who, when traveling with the military have been barred from using less secure systems that are easier to track. P = 30+0.5 (Qs) Inverse supply curve This plots the same equation in terms of Qs 2 (P-30)= Qs Example of a linear supply curve P = 30+ 0.5 (QS) WebShort Run Supply Curve of a Firm Let us derive a short-run supply curve for an enterprise. Price in a perfectly competitive industry is determined by the interaction of demand and supply. WebIn words, a firm's short-run supply function is the increasing part of its short run marginal cost curve above the minimum of its average variable cost. We shall divide this derivation into two parts.
New customers included the U.S. and British militaries, as well as reporters in Iraq, who, when traveling with the military have been barred from using less secure systems that are easier to track. P = 30+0.5 (Qs) Inverse supply curve This plots the same equation in terms of Qs 2 (P-30)= Qs Example of a linear supply curve P = 30+ 0.5 (QS) WebShort Run Supply Curve of a Firm Let us derive a short-run supply curve for an enterprise. Price in a perfectly competitive industry is determined by the interaction of demand and supply. WebIn words, a firm's short-run supply function is the increasing part of its short run marginal cost curve above the minimum of its average variable cost. We shall divide this derivation into two parts.
The equilibrium price is $0.40 per pound; the equilibrium quantity is 10 million pounds per month. Anything that makes production more expensive or more difficult, or any belief by firms that this will happen, will cause the SRAS to shift to the left. WebThis supply curve, based as it is on the short-run marginal cost curves of the firms in the industry, is the industrys short-run supply curve. As the market price rises, the firm will supply more of its product, in accordance with the law of supply. In the market for radishes, the equilibrium price is $0.40 per pound; 10 million pounds per month are produced and purchased at this price. Explain when a firm will shut down in the short run and when it will operate even if it is incurring economic losses. Structured Query Language (known as SQL) is a programming language used to interact with a database. Excel Fundamentals - Formulas for Finance, Certified Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA), Business Intelligence & Data Analyst (BIDA), Commercial Real Estate Finance Specialization, Environmental, Social & Governance Specialization, Cryptocurrency & Digital Assets Specialization (CDA), Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA), Financial Planning & Wealth Management Professional (FPWM). Direct link to upoma rahman's post How does subsidy affect t, Posted 3 years ago. In perfect competition, a firms marginal revenue curve is a horizontal line at the market price.
How Much Does Respite Foster Care Pay Texas?, List Of Inmates Being Released In Washington State, Tj Parker Park City Utah, Vendzor Games Worlds Hardest Game, Articles S