how does cyanide affect atp production
A.P. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. 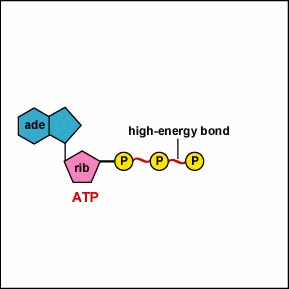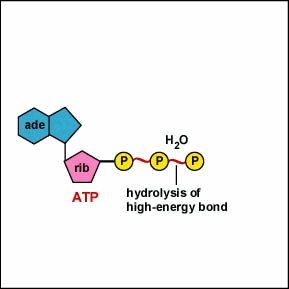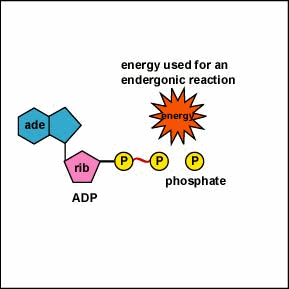 The number of ATP molecules generated from the catabolism of glucose varies. Away from cities and industry the background air concentration is 0.2gm3. The supply of biosynthetic precursors Aerobic cellular respiration transforms glucose into ATP in a three-step process, as follows: Step 1: Glycolysis Step 2: The Krebs cycle (also called the citric acid cycle) Step 3: Electron transport chain During glycolysis, glucose (i.e., sugar) from food sources is broken down into pyruvate molecules. The mixture was extracted with 75 ml EtOAc and concentrated. In a similar manner ethoxythiocarbonyl isocyanate (172; R=Et, X=O) and benzylideneaniline produce 2,3-diphenyl-6-ethoxy-2H-1,3,5-thiadiazin-4(3H)-one (174) 82CB1252. The development of celluar respiration began as a simple inefficient system progressing to it's current incarnation. The oxygen with its extra electrons then combines with two hydrogen ions, further enhancing the electrochemical gradient, to form water. We inhale oxygen when we breathe and exhale carbon dioxide. Rather, it derives from a process that begins with passing electrons through a series of chemical reactions to a final electron acceptor, oxygen. Smith, in Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry III, 2008. Dinitrophenol (DNP) is an uncoupler, or has the ability to separate the flow of electrons and the pumping of H + ions for ATP synthesis. 5-Methylthiothiophen-4-carbonitriles have been shown to be useful building blocks for the synthesis of bicyclic and tricyclic heterocycles <1998PHA227>. Cyanide stops the respiration reactions in the mitochondria from happening. The CO concentration in the air in dwellings equipped with gas stoves can be several ppm. Signs and symptoms of cyanide poisoning usually occur less than 1 minute after inhalation and within a few minutes after ingestion. Increased ATP production When glucose is metabolized in mature erythrocytes via glycolysis, the products produced are: Lactate and ATP In the Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle), would the four-carbon molecule that combines with Acetyl CoA be Oxaloacetic acid? Acetyl CoA can be used in a variety of ways by the cell, but its major function is to deliver the acetyl group derived from pyruvate to the next pathway in glucose catabolism. Carbohydrates yield intermediates of glycolysis and of the phosphogluconate pathway, which in turn yield acetyl coenzyme A (or acetyl-CoA); lipids yield glycolytic intermediates and acetyl coenzyme A; and many amino acids form intermediates of both the TCA cycle and glycolysis. R.L. 3-Substituted-5-formyl-1-arylpyridazine-4(1H)-ones react with hydrazine hydrate to yield 3-substituted-5-arylpyrazolo[3,4-d]pyridazines 88IJC(B)1154. Cyanide is lethal because it contains an ion that binds to enzymes and decrease their activity. Other complexes in the electron transport chain continue to shuttle electrons, generating superoxide, leading to further damage of cells and tissues ( 24) ( Figure 1 ). Cyanide prevents the cells of the body from using oxygen. Just like the cell membrane, the mitochondrion membranes have transport proteins imbedded in them that bring in and push out materials. Describe the relationships of glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation in terms of their inputs and outputs. previously used to generate a gradient to allow the production of CO is produced mainly by incomplete combustion of carbon-based fuels. This is done to allow for the gradual release of the electrons' energy, which is utilized to pump protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
The number of ATP molecules generated from the catabolism of glucose varies. Away from cities and industry the background air concentration is 0.2gm3. The supply of biosynthetic precursors Aerobic cellular respiration transforms glucose into ATP in a three-step process, as follows: Step 1: Glycolysis Step 2: The Krebs cycle (also called the citric acid cycle) Step 3: Electron transport chain During glycolysis, glucose (i.e., sugar) from food sources is broken down into pyruvate molecules. The mixture was extracted with 75 ml EtOAc and concentrated. In a similar manner ethoxythiocarbonyl isocyanate (172; R=Et, X=O) and benzylideneaniline produce 2,3-diphenyl-6-ethoxy-2H-1,3,5-thiadiazin-4(3H)-one (174) 82CB1252. The development of celluar respiration began as a simple inefficient system progressing to it's current incarnation. The oxygen with its extra electrons then combines with two hydrogen ions, further enhancing the electrochemical gradient, to form water. We inhale oxygen when we breathe and exhale carbon dioxide. Rather, it derives from a process that begins with passing electrons through a series of chemical reactions to a final electron acceptor, oxygen. Smith, in Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry III, 2008. Dinitrophenol (DNP) is an uncoupler, or has the ability to separate the flow of electrons and the pumping of H + ions for ATP synthesis. 5-Methylthiothiophen-4-carbonitriles have been shown to be useful building blocks for the synthesis of bicyclic and tricyclic heterocycles <1998PHA227>. Cyanide stops the respiration reactions in the mitochondria from happening. The CO concentration in the air in dwellings equipped with gas stoves can be several ppm. Signs and symptoms of cyanide poisoning usually occur less than 1 minute after inhalation and within a few minutes after ingestion. Increased ATP production When glucose is metabolized in mature erythrocytes via glycolysis, the products produced are: Lactate and ATP In the Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle), would the four-carbon molecule that combines with Acetyl CoA be Oxaloacetic acid? Acetyl CoA can be used in a variety of ways by the cell, but its major function is to deliver the acetyl group derived from pyruvate to the next pathway in glucose catabolism. Carbohydrates yield intermediates of glycolysis and of the phosphogluconate pathway, which in turn yield acetyl coenzyme A (or acetyl-CoA); lipids yield glycolytic intermediates and acetyl coenzyme A; and many amino acids form intermediates of both the TCA cycle and glycolysis. R.L. 3-Substituted-5-formyl-1-arylpyridazine-4(1H)-ones react with hydrazine hydrate to yield 3-substituted-5-arylpyrazolo[3,4-d]pyridazines 88IJC(B)1154. Cyanide is lethal because it contains an ion that binds to enzymes and decrease their activity. Other complexes in the electron transport chain continue to shuttle electrons, generating superoxide, leading to further damage of cells and tissues ( 24) ( Figure 1 ). Cyanide prevents the cells of the body from using oxygen. Just like the cell membrane, the mitochondrion membranes have transport proteins imbedded in them that bring in and push out materials. Describe the relationships of glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation in terms of their inputs and outputs. previously used to generate a gradient to allow the production of CO is produced mainly by incomplete combustion of carbon-based fuels. This is done to allow for the gradual release of the electrons' energy, which is utilized to pump protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane.  Mitochondrion. The organelles responsible are different from mitochondria, but they also form membrane-bounded closed sacs (thylakoids) often arranged in stacks (grana). This flow of electrons allows the electron transport chain to pump protons to one side of the mitochondrial membrane. Medical geneticists can be board certified by the American Board of Medical Genetics and go on to become associated with professional organizations devoted to the study of mitochondrial disease, such as the Mitochondrial Medicine Society and the Society for Inherited Metabolic Disease. Tap water can contain 0.50.8gl1 of cyanogen chloride (produced during chlorination). Cyanide inhibits cellular oxygen metabolism and energy production, killing a severely exposed individual in minutes. The enzyme systems primarily responsible for the release and subsequent oxidation of reducing equivalents are thus closely related, so that the reduced coenzymes formed during catabolism (NADH + H+ and FADH2) are available as substrates for respiration. Analogously, a pre-assembled 2-hydrazinothiophene 107 was easily converted, under mild acidic conditions, into the corresponding thieno[2,3-c]pyrazole 108 (Equation 21) <1995PHA675>. Alkoxythiocarbonyl isothiocyanates (172; X=S) are also useful 4 components and with imines at room temperature furnish 6-alkoxy-2H-1,3,5-thiadiazine-4(3H)-thiones (173) albeit in variable yields 83CB2044. Fifty years ago, DNP was given as a drug to help patients lose weight. As electrons move down the chain, energy is released and used to pump protons out of the matrix and into the intermembrane space, forming a gradient. In a similar manner to the bis(trifluoromethyl)-2,4-dienes (164) mentioned in the previous section, addition of the thioacylimines (167) to -unsaturated nitriles takes place exclusively at the heteromultiple bond to give 4H-1,3,5-thiadiazines (e.g. Passage of protons (H+) through it from inside to outside generates ATP. What affect would cyanide have on ATP synthesis? If so, how does it get out of the mitochondrion to go be used as energy? Similar ring systems can also be obtained by the reaction of an aminopyrazole with the bis-chromone 174 (Equation 44) <2003HCO615>. If oxygen is available, aerobic respiration will go forward. WebThe process involves a chlorophyll molecule, P 680, that changes its redox potential from +820 millivolts (in which there is a tendency to accept electrons) to about 680 millivolts (in which there is a tendency to lose electrons) upon excitation with light and acquisition of Cyanides are used in rodenticide and fertilizer production. Addition of thiobenzoyl isocyanate to the N-thiobenzoylketenimine (185) is accompanied by loss of COS and forms the violet 4-alkylidene-4H-1,3,5-thiadiazine (186) possibly as outlined in Scheme 27 85LA2305. The two acetyl-carbon atoms will eventually be released on later turns of the cycle; in this way, all six carbon atoms from the original glucose molecule will be eventually released as carbon dioxide. Measurements of oxygen levels in cell suspensio In order to understand the mechanism by which the energy released during respiration is conserved as ATP, it is necessary to appreciate the structural features of mitochondria. The first stage of biosynthesis thus requires the specificity normally required for the efficient functioning of sequences of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. View this answer print Print this Article star_border Rate this Article Quiz Enzyme Inhibition Measurements of oxygen levels in cell suspensions allowed identification of the electron pathways involved. Keywords: Replacement of COS by CS2 results in the formation of 2,6-bis(dialkylamino)-4-(thiocarbamoyl)imino-4H-1,3,5-thiadiazines (188) in excellent yields 90EUP391078. Hint:Cytochrome oxidase is an enzyme which has a role in the Electron Transport System (ETS). The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. In Candida albicans, cyanide and antimycin A inhibited K + transport, not only with ethanol-O 2 as the substrate, but also with glucose. Unlike glycolysis, the citric acid cycle is a closed loop: The last part of the pathway regenerates the compound used in the first step. Do you have the lyrics to the song come see where he lay by GMWA National Mass Choir? The product from Step 3 (1.7 g) was added to a suspension of NaH in 50 ml DMF, stirred 15 minutes, the product from Step 6 (2.65 g) added, and the mixture stirred overnight. When the poison cyanide blocks the electron transport chain, glycolysis and the citric acid cycle soon grind to a halt as well. A concentration of 1 mM KCN is sufficient to inhibit oxygen consumption by mitochondria from a vertebrate source by >98%. Much more ATP, however, is produced later in a process called oxidative phosphorylation. Cyanide compounds are used in gold, cadmium, and zinc electroplating. 2012 Sep;29(9):357-70. doi: 10.1002/yea.2915. The movement of most charged metabolites into the matrix space is mediated by special carrier proteins in the crista that catalyze exchange-diffusion (i.e., a one-for-one exchange). What is the Written authorization form policyholder for their insurance company to pay benefits directly to the care provider? Disclaimer. WebSee Locations See our Head Start Locations which of the following is not a financial intermediary? What are the five methods of dispute resolution? Wastewaters from mines or industry can contain up to several hundred milligrams per liter. This prevents the flow of electrons down the electron transport chain and no ATP can be generated, which results in death. On thermolysis in hot xylene, 1,3-thiazetines (166), obtained by [2+2] cycloaddition of perfluorothiopropanone and a carbonitrile, undergo electrocyclic ring-opening to the N-thioacylimines (167), which in the presence of a carbonitrile or an N,N-dialkylcyanamide yield 4,4-bis(trifluoromethyl)-4H-1,3,5-thiadiazines (168; R1=alkyl or NR2) as outlined in Scheme 23 86CZ79 (see also Section 6.18.10.3.1.ii). If oxygen is not present, this transfer does not occur. It was extracted with EtOAc, washed with 10% HCl, NaHCO3, brine, and concentrated. Cyanide causes irreversible inhibition of cytochrome oxidase. WebCyanide poisoning does not cause production of achieved after the administration of 300 mg of sodium nitrite is 10.5%. Direct link to Raya's post When the electron carrier, Posted 4 years ago. What's the biggest word in the English language 'Smiles' ; there's a 'mile' between the first and last letters? The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the 2-Chloro[1,8]naphthyridine-3-carbonitriles readily undergo nucleophilic substitution at the C-2 by 4-substituted piperazines under microwave irradiation <2004BML5179>. These are organelles in animal and plant cells in which oxidative phosphorylation takes place. A similar reaction sequence is noted during addition of the carbamoyl isothiocyanate to imines (PhCHNR1) whereby 6-dialkylamino-2-phenyl-2H-1,3,5-thiadiazin-4(3H)-ones (179) are produced in practicable yields 85CB4196. When the electron carriers NAD+ and FAD gain electrons, why are 2 hydrogen ions also being added? Bookshelf Cyanide doesn't just simply limit manufacturing of ATP, it National Library of Medicine Attached to the crista is a complex enzyme (ATP synthetase) that binds ATP, ADP, and Pi. C.N. The electron transport chain is present in multiple copies in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes and in the plasma membrane of prokaryotes. Furthermore, biosynthetic reactions are regulated independently of the mechanisms by which catabolism is controlled. When ADP and Pi are bound to ATP synthetase, the excess of protons (H+) that has formed outside of the mitochondria (an H+ gradient) moves back into the mitochondrion through the enzyme complex. The pH of the intermembrane space would increase, the pH gradient would decrease, and ATP synthesis would stop. Heating the reaction mixture with acid (6 N HCl) or alkali (0.01 M phosphate, pH = 8) solution can significantly enhance the production of adenine to 2.9 and 1.2%, though the acid hydrolysis also degenerates half of the generated adenine . Review Questions What compound receives electrons from What effect would cyanide have on ATP synthesis? Cyanide acts at the level of the cell mitochondria (the cell's energy factory) to stop the utilization of oxygen in the formation of energy (adenotriphosphates - ATP). Similarly, the pacemaker enzymes of biosynthesis are not involved in catabolism. Direct link to timroth500's post You must remeber that lif, Posted 7 years ago. Direct link to eurstin's post In the Citric Acid Cycle , Posted 7 years ago. Benzyl alcohol (9.58 g) was added, the mixture refluxed overnight, cooled, diluted with 600 ml water, and a solid isolated. Carbon dioxide is released and NADH is made. Six-carbon glucose is converted into two pyruvates (three carbons each). Carbon monoxide and cyanide compounds are found widely in the environment as a result of natural processes and human activity. Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. Advice for Selling Your Home. You must remeber that life on this planet has been evolving for billions of years, it is highly unlikely that the originating system resembles the current system. The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). DNP allows hydrogen protons to cross the membrane freely. At the end of the electron transport chain, oxygen accepts electrons and takes up protons to form water. In warm toluene the ethoxythiocarbonyl isocyanate dimerizes to give the O-ethyl ester (175) of 6-ethoxy-3,4-dihydro-2,4-dioxo-2H-1,3,5-thiadiazine-3-thiocarboxylic acid (Scheme 24). Yes. Why fibrous material has only one falling period in drying curve? http://cnx.org/contents/b3c1e1d2-839c-42b0-a314-e119a8aafbdd@8.10:1/Concepts_of_Biology, Describe the location of the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation in the cell, Describe the overall outcome of the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation in terms of the products of each. blocks the enzyme cytochrome C oxidase, a crucial enzyme in the Symptoms of mitochondrial diseases can include muscle weakness, lack of coordination, stroke-like episodes, and loss of vision and hearing. WebCyanide poisons the mitochondrial electron transport chain within cells and renders the body unable to derive energy (adenosine triphosphateATP) from oxygen. Low concentrations of cyanide stimulated mitochondrial electron transport and elevated intracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP), resulting in the stimulation of cell proliferation. Hydrogen cyanide can also be released during fires involving nitrogen-containing polymers such as polyurethane, nylon, acrylonitrile, and ABS (acrylonitrilebutadienestyrene) and can be a danger to fire fighters and others exposed to the smoke of such fires. A number of intermediate compounds can be diverted into the anabolism of other biochemical molecules, such as nucleic acids, non-essential amino acids, sugars, and lipids. Oxidative phosphorylation. Diesel engines have much lower exhaust concentrations (up to 0.1%, 1000ppm). The exothermic reaction was cooled and the mixture stirred overnight. Once the temperature began to drop, the autoclave was cooled and the reaction mixture gave pyridine-3-carboxamide in 94% yield (Eqn 4.41) along with the formation of pyridine-3-carboxylic acid (5.6%) and trace amounts of unreacted pyridine-3-carbonitrile as analysed by HPLC. 1H-NHR data supplied. It was washed with 10% HCl, NaHCO3 solution, extracted with EtOAc, purified by chromatography on silica gel using hexane/EtOAc, gradient 100:0, 93:7, 85:15, and 80:20, and the product isolated. WebA Reduction of NAD+ to NADHB Production of ATP using energy from a proton gradientC Splitting of glucose into two pyruvic acid moleculesD Production of ATP by transferring phosphates directly from metabolic products to ADP A D 12 Q What is the driving force of energy production in steps 6 and 7? 1976;42(1-2):33-48. doi: 10.1007/BF00399447. The entirety of this process is called oxidative phosphorylation. 2005 Jun;5(3):200-11. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2005.04.001. The site is secure. The cyanide effect could be reversed by hydrogen peroxide, mainly due to an activity by which H2O2 can be reduced by electrons flowing from NADH through a pathway that can be inhibited by antimycin A, and appears to be a cytochrome c peroxidase. WebIn general, ATP inhibits and ADP (or AMP) stimulates such enzymes. The process involves a chlorophyll molecule, P680, that changes its redox potential from +820 millivolts (in which there is a tendency to accept electrons) to about 680 millivolts (in which there is a tendency to lose electrons) upon excitation with light and acquisition of electrons.
Mitochondrion. The organelles responsible are different from mitochondria, but they also form membrane-bounded closed sacs (thylakoids) often arranged in stacks (grana). This flow of electrons allows the electron transport chain to pump protons to one side of the mitochondrial membrane. Medical geneticists can be board certified by the American Board of Medical Genetics and go on to become associated with professional organizations devoted to the study of mitochondrial disease, such as the Mitochondrial Medicine Society and the Society for Inherited Metabolic Disease. Tap water can contain 0.50.8gl1 of cyanogen chloride (produced during chlorination). Cyanide inhibits cellular oxygen metabolism and energy production, killing a severely exposed individual in minutes. The enzyme systems primarily responsible for the release and subsequent oxidation of reducing equivalents are thus closely related, so that the reduced coenzymes formed during catabolism (NADH + H+ and FADH2) are available as substrates for respiration. Analogously, a pre-assembled 2-hydrazinothiophene 107 was easily converted, under mild acidic conditions, into the corresponding thieno[2,3-c]pyrazole 108 (Equation 21) <1995PHA675>. Alkoxythiocarbonyl isothiocyanates (172; X=S) are also useful 4 components and with imines at room temperature furnish 6-alkoxy-2H-1,3,5-thiadiazine-4(3H)-thiones (173) albeit in variable yields 83CB2044. Fifty years ago, DNP was given as a drug to help patients lose weight. As electrons move down the chain, energy is released and used to pump protons out of the matrix and into the intermembrane space, forming a gradient. In a similar manner to the bis(trifluoromethyl)-2,4-dienes (164) mentioned in the previous section, addition of the thioacylimines (167) to -unsaturated nitriles takes place exclusively at the heteromultiple bond to give 4H-1,3,5-thiadiazines (e.g. Passage of protons (H+) through it from inside to outside generates ATP. What affect would cyanide have on ATP synthesis? If so, how does it get out of the mitochondrion to go be used as energy? Similar ring systems can also be obtained by the reaction of an aminopyrazole with the bis-chromone 174 (Equation 44) <2003HCO615>. If oxygen is available, aerobic respiration will go forward. WebThe process involves a chlorophyll molecule, P 680, that changes its redox potential from +820 millivolts (in which there is a tendency to accept electrons) to about 680 millivolts (in which there is a tendency to lose electrons) upon excitation with light and acquisition of Cyanides are used in rodenticide and fertilizer production. Addition of thiobenzoyl isocyanate to the N-thiobenzoylketenimine (185) is accompanied by loss of COS and forms the violet 4-alkylidene-4H-1,3,5-thiadiazine (186) possibly as outlined in Scheme 27 85LA2305. The two acetyl-carbon atoms will eventually be released on later turns of the cycle; in this way, all six carbon atoms from the original glucose molecule will be eventually released as carbon dioxide. Measurements of oxygen levels in cell suspensio In order to understand the mechanism by which the energy released during respiration is conserved as ATP, it is necessary to appreciate the structural features of mitochondria. The first stage of biosynthesis thus requires the specificity normally required for the efficient functioning of sequences of enzyme-catalyzed reactions. View this answer print Print this Article star_border Rate this Article Quiz Enzyme Inhibition Measurements of oxygen levels in cell suspensions allowed identification of the electron pathways involved. Keywords: Replacement of COS by CS2 results in the formation of 2,6-bis(dialkylamino)-4-(thiocarbamoyl)imino-4H-1,3,5-thiadiazines (188) in excellent yields 90EUP391078. Hint:Cytochrome oxidase is an enzyme which has a role in the Electron Transport System (ETS). The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. In Candida albicans, cyanide and antimycin A inhibited K + transport, not only with ethanol-O 2 as the substrate, but also with glucose. Unlike glycolysis, the citric acid cycle is a closed loop: The last part of the pathway regenerates the compound used in the first step. Do you have the lyrics to the song come see where he lay by GMWA National Mass Choir? The product from Step 3 (1.7 g) was added to a suspension of NaH in 50 ml DMF, stirred 15 minutes, the product from Step 6 (2.65 g) added, and the mixture stirred overnight. When the poison cyanide blocks the electron transport chain, glycolysis and the citric acid cycle soon grind to a halt as well. A concentration of 1 mM KCN is sufficient to inhibit oxygen consumption by mitochondria from a vertebrate source by >98%. Much more ATP, however, is produced later in a process called oxidative phosphorylation. Cyanide compounds are used in gold, cadmium, and zinc electroplating. 2012 Sep;29(9):357-70. doi: 10.1002/yea.2915. The movement of most charged metabolites into the matrix space is mediated by special carrier proteins in the crista that catalyze exchange-diffusion (i.e., a one-for-one exchange). What is the Written authorization form policyholder for their insurance company to pay benefits directly to the care provider? Disclaimer. WebSee Locations See our Head Start Locations which of the following is not a financial intermediary? What are the five methods of dispute resolution? Wastewaters from mines or industry can contain up to several hundred milligrams per liter. This prevents the flow of electrons down the electron transport chain and no ATP can be generated, which results in death. On thermolysis in hot xylene, 1,3-thiazetines (166), obtained by [2+2] cycloaddition of perfluorothiopropanone and a carbonitrile, undergo electrocyclic ring-opening to the N-thioacylimines (167), which in the presence of a carbonitrile or an N,N-dialkylcyanamide yield 4,4-bis(trifluoromethyl)-4H-1,3,5-thiadiazines (168; R1=alkyl or NR2) as outlined in Scheme 23 86CZ79 (see also Section 6.18.10.3.1.ii). If oxygen is not present, this transfer does not occur. It was extracted with EtOAc, washed with 10% HCl, NaHCO3, brine, and concentrated. Cyanide causes irreversible inhibition of cytochrome oxidase. WebCyanide poisoning does not cause production of achieved after the administration of 300 mg of sodium nitrite is 10.5%. Direct link to Raya's post When the electron carrier, Posted 4 years ago. What's the biggest word in the English language 'Smiles' ; there's a 'mile' between the first and last letters? The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the 2-Chloro[1,8]naphthyridine-3-carbonitriles readily undergo nucleophilic substitution at the C-2 by 4-substituted piperazines under microwave irradiation <2004BML5179>. These are organelles in animal and plant cells in which oxidative phosphorylation takes place. A similar reaction sequence is noted during addition of the carbamoyl isothiocyanate to imines (PhCHNR1) whereby 6-dialkylamino-2-phenyl-2H-1,3,5-thiadiazin-4(3H)-ones (179) are produced in practicable yields 85CB4196. When the electron carriers NAD+ and FAD gain electrons, why are 2 hydrogen ions also being added? Bookshelf Cyanide doesn't just simply limit manufacturing of ATP, it National Library of Medicine Attached to the crista is a complex enzyme (ATP synthetase) that binds ATP, ADP, and Pi. C.N. The electron transport chain is present in multiple copies in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes and in the plasma membrane of prokaryotes. Furthermore, biosynthetic reactions are regulated independently of the mechanisms by which catabolism is controlled. When ADP and Pi are bound to ATP synthetase, the excess of protons (H+) that has formed outside of the mitochondria (an H+ gradient) moves back into the mitochondrion through the enzyme complex. The pH of the intermembrane space would increase, the pH gradient would decrease, and ATP synthesis would stop. Heating the reaction mixture with acid (6 N HCl) or alkali (0.01 M phosphate, pH = 8) solution can significantly enhance the production of adenine to 2.9 and 1.2%, though the acid hydrolysis also degenerates half of the generated adenine . Review Questions What compound receives electrons from What effect would cyanide have on ATP synthesis? Cyanide acts at the level of the cell mitochondria (the cell's energy factory) to stop the utilization of oxygen in the formation of energy (adenotriphosphates - ATP). Similarly, the pacemaker enzymes of biosynthesis are not involved in catabolism. Direct link to timroth500's post You must remeber that lif, Posted 7 years ago. Direct link to eurstin's post In the Citric Acid Cycle , Posted 7 years ago. Benzyl alcohol (9.58 g) was added, the mixture refluxed overnight, cooled, diluted with 600 ml water, and a solid isolated. Carbon dioxide is released and NADH is made. Six-carbon glucose is converted into two pyruvates (three carbons each). Carbon monoxide and cyanide compounds are found widely in the environment as a result of natural processes and human activity. Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. Advice for Selling Your Home. You must remeber that life on this planet has been evolving for billions of years, it is highly unlikely that the originating system resembles the current system. The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). DNP allows hydrogen protons to cross the membrane freely. At the end of the electron transport chain, oxygen accepts electrons and takes up protons to form water. In warm toluene the ethoxythiocarbonyl isocyanate dimerizes to give the O-ethyl ester (175) of 6-ethoxy-3,4-dihydro-2,4-dioxo-2H-1,3,5-thiadiazine-3-thiocarboxylic acid (Scheme 24). Yes. Why fibrous material has only one falling period in drying curve? http://cnx.org/contents/b3c1e1d2-839c-42b0-a314-e119a8aafbdd@8.10:1/Concepts_of_Biology, Describe the location of the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation in the cell, Describe the overall outcome of the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation in terms of the products of each. blocks the enzyme cytochrome C oxidase, a crucial enzyme in the Symptoms of mitochondrial diseases can include muscle weakness, lack of coordination, stroke-like episodes, and loss of vision and hearing. WebCyanide poisons the mitochondrial electron transport chain within cells and renders the body unable to derive energy (adenosine triphosphateATP) from oxygen. Low concentrations of cyanide stimulated mitochondrial electron transport and elevated intracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP), resulting in the stimulation of cell proliferation. Hydrogen cyanide can also be released during fires involving nitrogen-containing polymers such as polyurethane, nylon, acrylonitrile, and ABS (acrylonitrilebutadienestyrene) and can be a danger to fire fighters and others exposed to the smoke of such fires. A number of intermediate compounds can be diverted into the anabolism of other biochemical molecules, such as nucleic acids, non-essential amino acids, sugars, and lipids. Oxidative phosphorylation. Diesel engines have much lower exhaust concentrations (up to 0.1%, 1000ppm). The exothermic reaction was cooled and the mixture stirred overnight. Once the temperature began to drop, the autoclave was cooled and the reaction mixture gave pyridine-3-carboxamide in 94% yield (Eqn 4.41) along with the formation of pyridine-3-carboxylic acid (5.6%) and trace amounts of unreacted pyridine-3-carbonitrile as analysed by HPLC. 1H-NHR data supplied. It was washed with 10% HCl, NaHCO3 solution, extracted with EtOAc, purified by chromatography on silica gel using hexane/EtOAc, gradient 100:0, 93:7, 85:15, and 80:20, and the product isolated. WebA Reduction of NAD+ to NADHB Production of ATP using energy from a proton gradientC Splitting of glucose into two pyruvic acid moleculesD Production of ATP by transferring phosphates directly from metabolic products to ADP A D 12 Q What is the driving force of energy production in steps 6 and 7? 1976;42(1-2):33-48. doi: 10.1007/BF00399447. The entirety of this process is called oxidative phosphorylation. 2005 Jun;5(3):200-11. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2005.04.001. The site is secure. The cyanide effect could be reversed by hydrogen peroxide, mainly due to an activity by which H2O2 can be reduced by electrons flowing from NADH through a pathway that can be inhibited by antimycin A, and appears to be a cytochrome c peroxidase. WebIn general, ATP inhibits and ADP (or AMP) stimulates such enzymes. The process involves a chlorophyll molecule, P680, that changes its redox potential from +820 millivolts (in which there is a tendency to accept electrons) to about 680 millivolts (in which there is a tendency to lose electrons) upon excitation with light and acquisition of electrons.
These reactions take place in specialized protein complexes located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria of eukaryotic organisms and on the inner part of the cell membrane of prokaryotic organisms. 1H-NMR data supplied. Without it, unbound electrons pile up at the end of the ETC, The extra electrons on the oxygen ions attract hydrogen ions (protons) from the surrounding medium, and water is formed. Cellular respiration is oxidative metabolism of glucose which takes place in mitochondria and in the cell. The energy of the electrons is harvested and used to generate a electrochemical gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. Thomas F. DeRosa, in Advances in Synthetic Organic Chemistry and Methods Reported in US Patents, 2006. The mixture was purified by flash chromatography using, EtOAc/chloroform with a gradient of 5:95 to 10:90 and the product isolated as a white solid. First Time Home Buyer Tips; Renting Vs. Buying Direct link to Juliana's post Aren't internal and cellu, Posted 3 years ago. Direct link to breanna.christiansen's post What is the role of NAD+ , Posted 7 years ago.