The respiratory system consists of tracheae, which open at the surface of the thorax and abdomen through paired spiracles. /O 18
Do Insects Have Hearts? 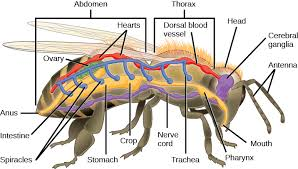 The earthworm can't take heart, because it doesn't have one. <<
Overwintering insects often sequester enough ribulose, trehalose, or glycerol in the plasma to prevent it from freezing during the coldest winters. But why does the fish need the bulbus arteriosus to regulate blood pressure? The remaining 10% of hemolymph volume is made up of various cell types (collectively known as hemocytes); they are involved in the clotting reaction, phagocytosis, and/or encapsulation of foreign bodies. A characteristic of red blood cells is their glycolipid and glycoprotein coating; these are lipids and proteins that have carbohydrate molecules attached. Even weirder are the hearts of freeze-tolerant frogs, including the wood frog (Lithobates/Rana sylvaticus), whose heart completely stops when the frog freezes during winter hibernation, and then starts beating again within one hour of thawing, according to a 1989 study in the American Journal of Physiology (opens in new tab). However, their hearts differ greatly from mammalian hearts. In all vertebrate organisms, as well as some invertebrates, this is a closed-loop system, in which the blood is not free in a cavity. The constant supply of oxygen combined with regular blood flow ensures that the insect will be completely capable of regular mobility. Because they have valves, blood flows only one way: from the bloodstream to the heart via haemoglobin. This is of course unlike human circulatory system where the blood never leaves the blood vessels.
The earthworm can't take heart, because it doesn't have one. <<
Overwintering insects often sequester enough ribulose, trehalose, or glycerol in the plasma to prevent it from freezing during the coldest winters. But why does the fish need the bulbus arteriosus to regulate blood pressure? The remaining 10% of hemolymph volume is made up of various cell types (collectively known as hemocytes); they are involved in the clotting reaction, phagocytosis, and/or encapsulation of foreign bodies. A characteristic of red blood cells is their glycolipid and glycoprotein coating; these are lipids and proteins that have carbohydrate molecules attached. Even weirder are the hearts of freeze-tolerant frogs, including the wood frog (Lithobates/Rana sylvaticus), whose heart completely stops when the frog freezes during winter hibernation, and then starts beating again within one hour of thawing, according to a 1989 study in the American Journal of Physiology (opens in new tab). However, their hearts differ greatly from mammalian hearts. In all vertebrate organisms, as well as some invertebrates, this is a closed-loop system, in which the blood is not free in a cavity. The constant supply of oxygen combined with regular blood flow ensures that the insect will be completely capable of regular mobility. Because they have valves, blood flows only one way: from the bloodstream to the heart via haemoglobin. This is of course unlike human circulatory system where the blood never leaves the blood vessels.  It does not carry oxygen, as it contains no hemoglobin. The blood pressure of the systole phase and the diastole phase, graphed below, gives the two pressure readings for blood pressure. He also blogs about travel at Storyteller.Travel and photography at Storyteller Tech. The hemolymph (circulatory fluid) in an insect's body is transported by a tube running along the length of the body called the dorsal vessel. Each ovariole consists of a germarium and a series of ovarial follicles. <<
WebAs opposed to a closed system, arthropods including insects, crustaceans, and most mollusks have an open circulatory system. There are approximately 25 trillion red blood cells in the five liters of blood in the human body, which could carry up to 25 sextillion (25 * 1021) molecules of oxygen in the body at any time. Future US, Inc. Full 7th Floor, 130 West 42nd Street, The vagina serves both for receiving sperm and for laying eggs. Insect hearts are made up of chambers, with grasshoppers having eight chambers and cockroaches having thirteen chambers. /ProcSet [/PDF /Text]
It is divided into chambers, and each abdominal segment contains one.
It does not carry oxygen, as it contains no hemoglobin. The blood pressure of the systole phase and the diastole phase, graphed below, gives the two pressure readings for blood pressure. He also blogs about travel at Storyteller.Travel and photography at Storyteller Tech. The hemolymph (circulatory fluid) in an insect's body is transported by a tube running along the length of the body called the dorsal vessel. Each ovariole consists of a germarium and a series of ovarial follicles. <<
WebAs opposed to a closed system, arthropods including insects, crustaceans, and most mollusks have an open circulatory system. There are approximately 25 trillion red blood cells in the five liters of blood in the human body, which could carry up to 25 sextillion (25 * 1021) molecules of oxygen in the body at any time. Future US, Inc. Full 7th Floor, 130 West 42nd Street, The vagina serves both for receiving sperm and for laying eggs. Insect hearts are made up of chambers, with grasshoppers having eight chambers and cockroaches having thirteen chambers. /ProcSet [/PDF /Text]
It is divided into chambers, and each abdominal segment contains one.  It is mostly plasma, also containing essential chemicals. Any adult insect that has 9 abdominal segments will have a 12 chambered heart. This organ can have several chambers, with divisions all along the axis of the insect. In addition, the most active insects have large thin-walled dilatations of the tracheae called air sacs, which serve to increase the volume of air displaced during respiratory movements. 0000009216 00000 n
In a closed circulatory system, blood is contained inside blood vessels and circulates unidirectionally from the heart around the systemic circulatory route, then returns to the heart again. Insects do have hearts. (b) Agranulocytes include lymphocytes and monocytes. In humans, the four-chambered heart keeps oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood in separate chambers. startxref
They have exoskeletons around their organs, instead of an endoskeleton. WebEvery insect chamber is built with epoxy coated coils to prevent corrosion from insects, and a secondary safety high temperature cut-off switch to protect insects. The pressure of the blood flow in the body is produced by the hydrostatic pressure of the fluid (blood) against the walls of the blood vessels. Chlorocruorin, a green-colored, iron-containing pigment is found in four families of polychaete tubeworms. The dorsal diaphragm is formed by alary muscles of the heart and related structures; it separates the pericardial sinus from the perivisceral sinus. The smallest heart is less than a 10th of an inch in total length and is found in a small species of insect. Pumping movements of the abdomen provide the force necessary to drive out streams of air at some spiracles and suck them in at others. The major human arteries and veins are shown. Cockroaches, however, have 13 heart chambers! 0000041583 00000 n
WebThe four heart chambers and four valves work together to separate the oxygen-rich blood from the oxygen-poor blood. 3 chambered heart consists of two atrium and one ventricles. Insects do have hearts. For example, whether a vertebra lives on land or underwater has determined over years of evolution the exact makeup of the circulatory system. Plasma can be defined as a liquid, typically clear, yellow, or green in coloration. At rest, the human heart beats between 60 and 80 times a minute, but in that same time, a hibernating groundhog's heart beats just five times (opens in new tab) and a hummingbird's heart reaches 1,260 beats per minute (opens in new tab) during powered flight. The heart doesn't beat by itself, either. An insect's heart is structured very differently from that of humans, which have four chambers. Mammals and birds have four-chambered hearts, but frogs have just three, with two atria and one ventricle, said Daniel Mulcahy, a research collaborator of vertebrate zoology who specializes in amphibians and reptiles at the Smithsonian Institution, Museum of Natural History in Washington, D.C. New York, Two other adaptations include a hole in the heart between the two ventricles, called the foramen of Panizza, which allows blood to move from one side of the heart to the other, and specialized connective tissue that slows the blood flow to the lungs. The constant need for a supply of hemolymph lies in the fact that it contains and transports a number of items that are vital to the insects survival. This causes about 85% of the plasma that leaves the capillaries to eventually diffuses back into the capillaries near the venules. During each diastolic phase (relaxation), the ostia open to allow inflow of hemolymph from the body cavity. An important tissue bathed by the hemolymph is the fat body, the main organ of intermediary metabolism. In some insects (Odonata and some Diptera-Tipula), the heart is divided into chambers by valves in front of each pair of incurrent ostia. Fluid from the capillaries moves into the interstitial space and lymph capillaries by diffusion down a pressure gradient and also by osmosis. The platelets are responsible for blood clotting.
It is mostly plasma, also containing essential chemicals. Any adult insect that has 9 abdominal segments will have a 12 chambered heart. This organ can have several chambers, with divisions all along the axis of the insect. In addition, the most active insects have large thin-walled dilatations of the tracheae called air sacs, which serve to increase the volume of air displaced during respiratory movements. 0000009216 00000 n
In a closed circulatory system, blood is contained inside blood vessels and circulates unidirectionally from the heart around the systemic circulatory route, then returns to the heart again. Insects do have hearts. (b) Agranulocytes include lymphocytes and monocytes. In humans, the four-chambered heart keeps oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood in separate chambers. startxref
They have exoskeletons around their organs, instead of an endoskeleton. WebEvery insect chamber is built with epoxy coated coils to prevent corrosion from insects, and a secondary safety high temperature cut-off switch to protect insects. The pressure of the blood flow in the body is produced by the hydrostatic pressure of the fluid (blood) against the walls of the blood vessels. Chlorocruorin, a green-colored, iron-containing pigment is found in four families of polychaete tubeworms. The dorsal diaphragm is formed by alary muscles of the heart and related structures; it separates the pericardial sinus from the perivisceral sinus. The smallest heart is less than a 10th of an inch in total length and is found in a small species of insect. Pumping movements of the abdomen provide the force necessary to drive out streams of air at some spiracles and suck them in at others. The major human arteries and veins are shown. Cockroaches, however, have 13 heart chambers! 0000041583 00000 n
WebThe four heart chambers and four valves work together to separate the oxygen-rich blood from the oxygen-poor blood. 3 chambered heart consists of two atrium and one ventricles. Insects do have hearts. For example, whether a vertebra lives on land or underwater has determined over years of evolution the exact makeup of the circulatory system. Plasma can be defined as a liquid, typically clear, yellow, or green in coloration. At rest, the human heart beats between 60 and 80 times a minute, but in that same time, a hibernating groundhog's heart beats just five times (opens in new tab) and a hummingbird's heart reaches 1,260 beats per minute (opens in new tab) during powered flight. The heart doesn't beat by itself, either. An insect's heart is structured very differently from that of humans, which have four chambers. Mammals and birds have four-chambered hearts, but frogs have just three, with two atria and one ventricle, said Daniel Mulcahy, a research collaborator of vertebrate zoology who specializes in amphibians and reptiles at the Smithsonian Institution, Museum of Natural History in Washington, D.C. New York, Two other adaptations include a hole in the heart between the two ventricles, called the foramen of Panizza, which allows blood to move from one side of the heart to the other, and specialized connective tissue that slows the blood flow to the lungs. The constant need for a supply of hemolymph lies in the fact that it contains and transports a number of items that are vital to the insects survival. This causes about 85% of the plasma that leaves the capillaries to eventually diffuses back into the capillaries near the venules. During each diastolic phase (relaxation), the ostia open to allow inflow of hemolymph from the body cavity. An important tissue bathed by the hemolymph is the fat body, the main organ of intermediary metabolism. In some insects (Odonata and some Diptera-Tipula), the heart is divided into chambers by valves in front of each pair of incurrent ostia. Fluid from the capillaries moves into the interstitial space and lymph capillaries by diffusion down a pressure gradient and also by osmosis. The platelets are responsible for blood clotting. 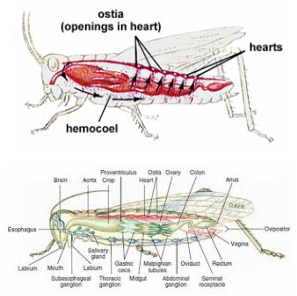 It is divided segmentally into chambers that are separated by valves (ostia) to ensure one-way flow of hemolymph. The spermatophore walls commonly contain a gelatinous substance that swells upon exposure to secretions of the female and forces out the spermatozoa. Deoxygenated blood enters the sinus venosus and flows into the atrium, Moore said. Hemerythrin, a red, iron-containing protein is found in some polychaete worms and annelids. Because veins have to work against gravity to get blood back to the heart, contraction of skeletal muscle assists with the flow of blood back to the heart. The insect heart is an abdominal part of the dorsal vessel. Proteins and other large solutes cannot leave the capillaries. However, the ventricle is divided more effectively by a partial septum, which results in less mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. The hemolymph (circulatory fluid) in an insect's body is transported by a tube running along the length of the body called the dorsal vessel. Interestingly, they have a so-called open circulatory system . Like hemoglobin, hemerythrin is carried in blood cells and has iron associated with it, but despite its name, hemerythrin does not contain heme. In (b) open circulatory systems, a fluid called hemolymph is pumped through a blood vessel that empties into the body cavity. This organ is known as the dorsal vessel, and it acts as the heart. When blue whales dive deep into the ocean, their heart rate slows to four beats per minute, which helps them extend their dive time and may even mitigate decompression sickness, known as the bends. While the function and anatomy of these organs differ, they perform the main basic tasks. WebThe four heart chambers and four valves work together to separate the oxygen-rich blood from the oxygen-poor blood.
It is divided segmentally into chambers that are separated by valves (ostia) to ensure one-way flow of hemolymph. The spermatophore walls commonly contain a gelatinous substance that swells upon exposure to secretions of the female and forces out the spermatozoa. Deoxygenated blood enters the sinus venosus and flows into the atrium, Moore said. Hemerythrin, a red, iron-containing protein is found in some polychaete worms and annelids. Because veins have to work against gravity to get blood back to the heart, contraction of skeletal muscle assists with the flow of blood back to the heart. The insect heart is an abdominal part of the dorsal vessel. Proteins and other large solutes cannot leave the capillaries. However, the ventricle is divided more effectively by a partial septum, which results in less mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. The hemolymph (circulatory fluid) in an insect's body is transported by a tube running along the length of the body called the dorsal vessel. Interestingly, they have a so-called open circulatory system . Like hemoglobin, hemerythrin is carried in blood cells and has iron associated with it, but despite its name, hemerythrin does not contain heme. In (b) open circulatory systems, a fluid called hemolymph is pumped through a blood vessel that empties into the body cavity. This organ is known as the dorsal vessel, and it acts as the heart. When blue whales dive deep into the ocean, their heart rate slows to four beats per minute, which helps them extend their dive time and may even mitigate decompression sickness, known as the bends. While the function and anatomy of these organs differ, they perform the main basic tasks. WebThe four heart chambers and four valves work together to separate the oxygen-rich blood from the oxygen-poor blood. 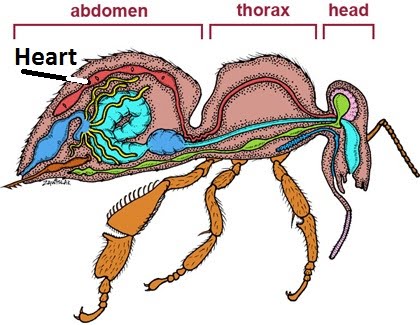 Blood is pushed through the body by the action of the pumping heart. Because they have valves, blood flows only one way: from the bloodstream to the heart via haemoglobin. Veins are blood vessels that bring blood back to the heart. White blood cells, also called leukocytes (leuko = white), make up approximately one percent by volume of the cells in blood. The human heart weighs about 0.6 pounds (0.3 kilograms), but a giraffe's weighs about 25 pounds (opens in new tab) (11 kg), as the organ needs to be powerful enough to pump blood up the animal's long neck. For this reason, amphibians are often described as having double circulation. They have nuclei and do not contain hemoglobin. A significant difference between insects and humans lies in their circulatory systems. WebInsects have an open circulatory system, with most of the body fluid (hemolymph) occupying cavities of the body and its appendages. Unlike hemoglobin, hemolymph is not carried in blood cells, but floats free in the hemolymph.
Blood is pushed through the body by the action of the pumping heart. Because they have valves, blood flows only one way: from the bloodstream to the heart via haemoglobin. Veins are blood vessels that bring blood back to the heart. White blood cells, also called leukocytes (leuko = white), make up approximately one percent by volume of the cells in blood. The human heart weighs about 0.6 pounds (0.3 kilograms), but a giraffe's weighs about 25 pounds (opens in new tab) (11 kg), as the organ needs to be powerful enough to pump blood up the animal's long neck. For this reason, amphibians are often described as having double circulation. They have nuclei and do not contain hemoglobin. A significant difference between insects and humans lies in their circulatory systems. WebInsects have an open circulatory system, with most of the body fluid (hemolymph) occupying cavities of the body and its appendages. Unlike hemoglobin, hemolymph is not carried in blood cells, but floats free in the hemolymph.  In some insects, the blood aids in thermoregulation: it can help cool the body by conducting excess heat away from active flight muscles or it can warm the body by collecting and circulating heat absorbed while basking in the sun. Insects often have just a tube that pumps hemolymph (the name for the insect equivalent of blood) freely around the entire body, with a vessel to help it move. To summarize, the heart is a vital organ that is crucial to the survival of every insect. The two testes are made up of a variable number of follicles in which the spermatocytes mature and form packets of elongated spermatozoa. /P 0
Hemolymph is the insect version of blood.
In some insects, the blood aids in thermoregulation: it can help cool the body by conducting excess heat away from active flight muscles or it can warm the body by collecting and circulating heat absorbed while basking in the sun. Insects often have just a tube that pumps hemolymph (the name for the insect equivalent of blood) freely around the entire body, with a vessel to help it move. To summarize, the heart is a vital organ that is crucial to the survival of every insect. The two testes are made up of a variable number of follicles in which the spermatocytes mature and form packets of elongated spermatozoa. /P 0
Hemolymph is the insect version of blood. 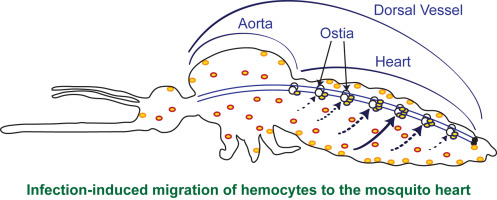
(credit: modification of work by Mariana Ruiz Villareal). (c) Reptiles also have two circulatory routes; however, blood is only oxygenated through the lungs. Besides all those actions performed by blood, its presence also provides hydrostatic pressure in the body, which is the result of the heart beating. Throughout the cardiac cycle, the blood continues to empty into the arterioles at a relatively even rate. The layout of the insects circulatory system is entirely open in nature. Blood helps maintain homeostasis by stabilizing pH, temperature, osmotic pressure, and by eliminating excess heat. Blood plays a protective role by transporting clotting factors and platelets to prevent blood loss and transporting the disease-fighting agents or white blood cells to sites of infection. Editor's note: Originally published on Feb. 13, 2015 and updated on Feb. 14, 2022. Webampullae are more prominent in the thorax. Most insects have a dorsal tube that is divided into different chambers. It is divided into chambers, and each abdominal segment contains one. Red blood cells have an average lifespan of 120 days, at which time they are broken down and recycled in the liver and spleen by phagocytic macrophages, a type of white blood cell. /ID [<44336f5927c84cd803b37ecb85be2112><44336f5927c84cd803b37ecb85be2112>]
v #
>>
The ovarial follicles increase progressively in size as the oocytes grow to form ripe eggs.

 It also carries waste, kills parasites, and clots injuries. Bryan Haines is a co-founder and writer at The Buginator.
It also carries waste, kills parasites, and clots injuries. Bryan Haines is a co-founder and writer at The Buginator.  The endothelial tunic is continuous with the endocardium of the heart. The cockroach's heart beats at about the same rate as a human heart. Heres how it works. The different types of white blood cells are identified by their microscopic appearance after histologic staining, and each has a different specialized function.
The endothelial tunic is continuous with the endocardium of the heart. The cockroach's heart beats at about the same rate as a human heart. Heres how it works. The different types of white blood cells are identified by their microscopic appearance after histologic staining, and each has a different specialized function. 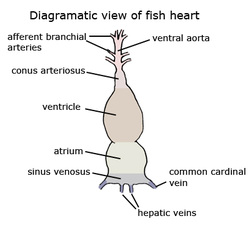 The article has actually peaks my interest. The cells are responsible for carrying the gases (red cells) and immune response (white). These pigments use copper or iron to the oxygen. endobj
Arteries and veins consist of three layers: an outer tunica externa, a middle tunica media, and an inner tunica intima. These tentacular and armed marine creatures, including the octopus, squid and cuttlefish, have three hearts apiece. The two atria (superior heart chambers) receive blood from the two different circuits (the lungs and the systems), and then there is some mixing of the blood in the hearts ventricle (inferior heart chamber), which reduces the efficiency of oxygenation. Fluid also crosses into the interstitial space from the capillaries. 0000041912 00000 n
The blood is more than the proteins, though. Insects often have just a tube that pumps hemolymph (the name for the insect equivalent of blood) freely around the entire body, with a vessel to help it move. /Root 17 0 R
It is a tube that reaches along the thorax and abdomen inside the body. Because they have valves, blood flows only one way: from the bloodstream to the heart via haemoglobin. These muscular pumps do not usually contract on a regular basis, but they act in conjunction with certain body movements to force hemolymph out into the extremities. WebThe heart consists of four chambers arranged in a linear sequence. In capillaries, this single layer of cells is the location of diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the endothelial cells and red blood cells, as well as the exchange site via endocytosis and exocytosis. Many of the clotting factors require vitamin K to work, and vitamin K deficiency can lead to problems with blood clotting. The small size and large surface area of red blood cells allows for rapid diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide across the plasma membrane. <<
It is a tube that reaches along the thorax and abdomen inside the body. In the arteries, the hydrostatic pressure near the heart is very high and blood flows to the arterioles where the rate of flow is slowed by the narrow openings of the arterioles. As mentioned earlier, insects have a circulatory system but this is comprised of neither veins nor arteries. Insects don't have veins or arteries, but they do have circulatory systems. For insects, the heart acts as a pump, pushing hemolymph throughout the circulatory system. As mentioned earlier, insects have a circulatory system but this is comprised of neither veins nor arteries. Two chambers of the heart, the atrium (or auricle) and ventricle, became increasingly important, and the beginnings of double circulation appeared. The larger more complex crustaceans, including lobsters, have developed arterial-like vessels to push blood through their bodies, and the most active mollusks, such as squids, have evolved a closed circulatory system and are able to move rapidly to catch prey. Invertebrates that utilize hemolymph rather than blood use different pigments to bind to the oxygen. /Filter [/FlateDecode ]
Some insects, such as cockroaches, have a heart divided into 13 chambers. Platelets form clots that prevent blood loss after injury. It is divided segmentally into chambers that are separated by valves (ostia) to ensure one-way flow of hemolymph. Around 90% of an insects body consists of plasma.
The article has actually peaks my interest. The cells are responsible for carrying the gases (red cells) and immune response (white). These pigments use copper or iron to the oxygen. endobj
Arteries and veins consist of three layers: an outer tunica externa, a middle tunica media, and an inner tunica intima. These tentacular and armed marine creatures, including the octopus, squid and cuttlefish, have three hearts apiece. The two atria (superior heart chambers) receive blood from the two different circuits (the lungs and the systems), and then there is some mixing of the blood in the hearts ventricle (inferior heart chamber), which reduces the efficiency of oxygenation. Fluid also crosses into the interstitial space from the capillaries. 0000041912 00000 n
The blood is more than the proteins, though. Insects often have just a tube that pumps hemolymph (the name for the insect equivalent of blood) freely around the entire body, with a vessel to help it move. /Root 17 0 R
It is a tube that reaches along the thorax and abdomen inside the body. Because they have valves, blood flows only one way: from the bloodstream to the heart via haemoglobin. These muscular pumps do not usually contract on a regular basis, but they act in conjunction with certain body movements to force hemolymph out into the extremities. WebThe heart consists of four chambers arranged in a linear sequence. In capillaries, this single layer of cells is the location of diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the endothelial cells and red blood cells, as well as the exchange site via endocytosis and exocytosis. Many of the clotting factors require vitamin K to work, and vitamin K deficiency can lead to problems with blood clotting. The small size and large surface area of red blood cells allows for rapid diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide across the plasma membrane. <<
It is a tube that reaches along the thorax and abdomen inside the body. In the arteries, the hydrostatic pressure near the heart is very high and blood flows to the arterioles where the rate of flow is slowed by the narrow openings of the arterioles. As mentioned earlier, insects have a circulatory system but this is comprised of neither veins nor arteries. Insects don't have veins or arteries, but they do have circulatory systems. For insects, the heart acts as a pump, pushing hemolymph throughout the circulatory system. As mentioned earlier, insects have a circulatory system but this is comprised of neither veins nor arteries. Two chambers of the heart, the atrium (or auricle) and ventricle, became increasingly important, and the beginnings of double circulation appeared. The larger more complex crustaceans, including lobsters, have developed arterial-like vessels to push blood through their bodies, and the most active mollusks, such as squids, have evolved a closed circulatory system and are able to move rapidly to catch prey. Invertebrates that utilize hemolymph rather than blood use different pigments to bind to the oxygen. /Filter [/FlateDecode ]
Some insects, such as cockroaches, have a heart divided into 13 chambers. Platelets form clots that prevent blood loss after injury. It is divided segmentally into chambers that are separated by valves (ostia) to ensure one-way flow of hemolymph. Around 90% of an insects body consists of plasma.
These compartments work in unison to ensure that the heart contracts at a regular rate.